

DPDK的提出以及设计思想是什么?
描述
01
vhost-user
DPDK的提出以及设计思想
随着各种互联网应用的不断出现,网络设备以及服务器的带宽也快速提升,从千兆到万兆再到25G,40G,100G快速演变。
与此同时,在云计算和系统虚拟化技术的快速发展的推动下,虚拟机的网络处理能力需求也逐年增强。
另外,不仅是在服务器领域,很多网络服务也都逐渐向虚拟化,资源池化,云化的方向发展,比如路由器,交换机,防火墙,基站等常用网络设备原本都是硬件解决方案,现在也逐渐向虚拟化方向发展,业界急需适合高性能网络的软件解决方案。
既往的基于Linux实现的网络服务是基于内核的,也就是说所有数据包的发送和接收都要经过内核协议栈。在处理大流量和高并发的情况下,频繁的硬件中断会降低内核数据包的处理能力,同时内核空间和用户空间之间的数据拷贝也会产生比较大的负载。
为了进一步提升网络数据处理能力,Linux UIO (user-space drivers) 技术把硬件操作映射到用户空间,实现了在用户空间直接操作网卡硬件。
这样网络数据包的处理就可以不经过Linux内核了,避免了高速网络数据处理时内核中断爆炸和大量数据复制的问题,进而让网络处理能力得以大幅度的提升。
绕过内核直接在用户态处理网络数据包,不仅可以解决内核的性能瓶颈,而且还易于开发和维护,和基于内核模块的实现相比也更灵活。
另外,因为程序运行在用户空间,即使有问题也不影响Linux内核和系统的其他模块,也增强了整个系统的可用性。
针对高性能网络软件开发框架的需求,基于Linux UIO技术在应用层处理网络数据包,这也正是Intel DPDK的主要设计思想。
DPDK应用初识
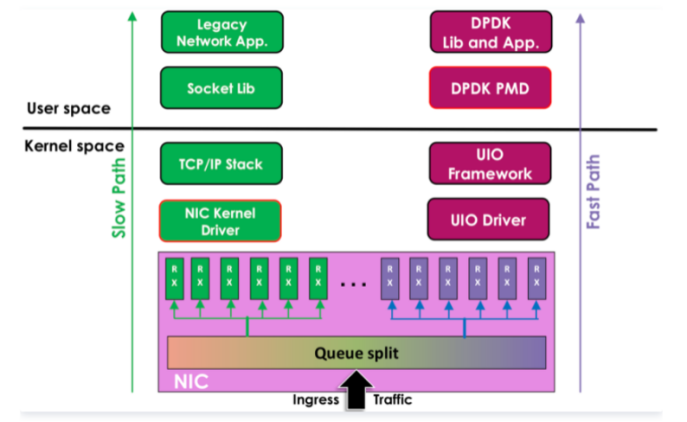
图1 Linux内核处理路径(慢路径)和DPDK处理路径(快路径)对比
如图1所表示的就是基于Linux内核的数据处理路径(慢路径)和基于DPDK的用户空间数据处理路径(快路径)的对比。
这里需要特别说明的是,Intel DPDK被编译之后其实是一系列的库文件,供应用程序调用和链接。基于DPDK机制开发的应用程序在编译和链接DPDK的库文件之后,就可以进行高速的网络处理了。
这些DPDK应用都是运行在用户空间的应用程序。通过Linux UIO的机制以及少量内核模块(例如Intel x86平台上需要预先加载igb_uio等内核驱动模块),这些运行在用户空间的DPDK应用程序能够旁路Linux内核,直接操作物理网卡进而完成高速网络数据的发送和接收。
截止到目前为止DPDK已经支持多种硬件体系结构,包括Intel x86,ARM,PowerPC等等,并且被网络设备厂商和互联网厂商广泛接受,已经有很多基于DPDK开发的产品和服务投入到生产环境使用了。
Intel DPDK的核心技术之一是PMD (用户态的轮询模式驱动)。通过非中断以及数据进出应用缓冲区内存的零拷贝机制,进一步提高发送接受数据的效率。用户态模式的PMD驱动,去除中断,避免内核态和用户态内存拷贝,减少系统开销,从而提升I/O吞吐能力。
我们可以通过分析DPDK中的L2fw程序,大致了解一下DPDK应用程序的基本结构。
具体的代码可以参考dpdk-stable-18.11.11/examples/l2fwd/main.c。l2fwd是一个简单的DPDK应用程序,可以看出在main函数中,调用rte_eal_init函数对DPDK运行环境进行初始化之后,调用l2fwd_launch_one_lcore函数在每个CPU的核上都运行l2fwd_main_loop函数。
l2fwd_main_loop函数就是在无限循环中不断的轮询该CPU核绑定的网卡的所有端口,调用rte_eth_tx_buffer_flush和 rte_eth_rx_burst进行数据包的发送和接收,进而再完成转发。
被DPDK应用绑定的CPU核不再被Linux内核调度,而是被l2fwd_main_loop函数独占。所以和原来基于Linux内核的实现相比,网络数据包的处理能力得以大幅度提升。 DPDK中的PMD技术的具体实现,可以参考dpdk-stable-18.11.11/drivers/net/e1000/igb_ethdev.c中的函数eth_igb_dev_init,PMD相关的实现是DPDK的内部实现,限于篇幅,我们这里就不展开讲解了。
|
int main(int argc, char **argv) { …… /* init EAL */ ret = rte_eal_init(argc, argv); if (ret < 0) …… /* launch per-lcore init on every lcore */ rte_eal_mp_remote_launch(l2fwd_launch_one_lcore, NULL, CALL_MASTER); …… } |
|
static int l2fwd_launch_one_lcore(__attribute__((unused)) void *dummy) { l2fwd_main_loop(); return 0; } |
|
/* main processing loop */ static void l2fwd_main_loop(void) { struct rte_mbuf *pkts_burst[MAX_PKT_BURST]; struct rte_mbuf *m; int sent; unsigned lcore_id; uint64_t prev_tsc, diff_tsc, cur_tsc, timer_tsc; unsigned i, j, portid, nb_rx; struct lcore_queue_conf *qconf; const uint64_t drain_tsc = (rte_get_tsc_hz() + US_PER_S - 1) / US_PER_S * BURST_TX_DRAIN_US; struct rte_eth_dev_tx_buffer *buffer; prev_tsc = 0; timer_tsc = 0; lcore_id = rte_lcore_id(); qconf = &lcore_queue_conf[lcore_id]; if (qconf->n_rx_port == 0) { RTE_LOG(INFO, L2FWD, "lcore %u has nothing to do ", lcore_id); return; } RTE_LOG(INFO, L2FWD, "entering main loop on lcore %u ", lcore_id); for (i = 0; i < qconf->n_rx_port; i++) { portid = qconf->rx_port_list[i]; RTE_LOG(INFO, L2FWD, " -- lcoreid=%u portid=%u ", lcore_id, portid); } while (!force_quit) { cur_tsc = rte_rdtsc(); /* * TX burst queue drain */ diff_tsc = cur_tsc - prev_tsc; if (unlikely(diff_tsc > drain_tsc)) { for (i = 0; i < qconf->n_rx_port; i++) { portid = l2fwd_dst_ports[qconf->rx_port_list[i]]; buffer = tx_buffer[portid]; sent = rte_eth_tx_buffer_flush(portid, 0, buffer); if (sent) port_statistics[portid].tx += sent; } /* if timer is enabled */ if (timer_period > 0) { /* advance the timer */ timer_tsc += diff_tsc; /* if timer has reached its timeout */ if (unlikely(timer_tsc >= timer_period)) { /* do this only on master core */ if (lcore_id == rte_get_master_lcore()) { print_stats(); /* reset the timer */ timer_tsc = 0; } } } prev_tsc = cur_tsc; } /* * Read packet from RX queues */ for (i = 0; i < qconf->n_rx_port; i++) { portid = qconf->rx_port_list[i]; nb_rx = rte_eth_rx_burst(portid, 0, pkts_burst, MAX_PKT_BURST); port_statistics[portid].rx += nb_rx; for (j = 0; j < nb_rx; j++) { m = pkts_burst[j]; rte_prefetch0(rte_pktmbuf_mtod(m, void *)); l2fwd_simple_forward(m, portid); } } } } |
vhost-user与DPDK
在对DPDK应用程序有了一个基本认识,并理解了基本原理和核心技术的基础上,下面我们进入到DPDK场景下用户态的virtio-net的实现,也就是vhost-user的相关介绍。
DPDK场景下,virtio-net后端和virtio-net前端的关系图,其中涉及到OVS-DPDK,QEMU,Linux内核和物理网卡硬件。我们接下来会先讲一下各个模块之间的关系,以及它们和virtio-net前端和后端的关系。
- OVS-DPDK:实现了三部分功能。1). 用户空间的PMD,不断地和物理网卡通信,发送接收数据包;2). 虚拟交换机的功能,这部分和我们平时熟悉的OVS是一样的;3). DPDK场景下的virtio-net后端的实现,和virtio-net前端通信。
- QEMU:是一个运行在用户空间的多线程程序,有运行虚拟机的vCPU线程,有处理中断的KVM线程和eventfd。不同之处在于:在DPDK场景下,virtio-net前端是运行在虚拟机线程内的DPDK应用程序。这时,虚拟机的网络接口的类型是vhost-user,它会基于UNIX domain socket和virtio-net后端(实现在OVS-DPDK中)通信。
可以看出,在DPDK场景下,virtio-net前端和后端的实现都在DPDK代码中。
在运行态的时候,就像图2所显示的那样,virtio-net前端是QEMU虚拟机内运行的DPDK应用程序,virtio-net后端运行在OVS-DPDK中。
两者都运行在用户态,通过UNIX domain socket进行通信。vhost-user是将virtio-net驱动在用户态的实现。
下面我们结合结合DPDK 18.11的代码,针对virtio设备的初始化,发送数据的处理流程,做进一步的分析和讲解。
设备发现和初始化
在QEMU虚拟机中运行DPDK应用时:virtio-net前端的初始化的具体实现是在dpdk-stable-18.11.11/drivers/net/virtio/virtio_ethdev.c文件中,其中rte_virtio_pmd是驱动的主要数据结构。
QEMU中的虚拟机运行DPDK应用程序的时候,在指定vhost-user端口的时候,会注册rte_virtio_pmd驱动程序。驱动中的probe函数注册为eth_virtio_pci_probe函数。DPDK驱动程序这样的写法和Linux内核中的PCI网络驱动是一样的,比较容易理解。
函数eth_virtio_dev_init会调用virtio_init_device函数,其中可以看到我们之前介绍过的复合virtio规范的协商特性位(feature bits),配置MTU等网卡相关的配置,调用virtio_alloc_queues配置虚拟队列等操作。
|
static struct rte_pci_driver rte_virtio_pmd = { .driver = { .name = "net_virtio", }, .id_table = pci_id_virtio_map, .drv_flags = 0, .probe = eth_virtio_pci_probe, .remove = eth_virtio_pci_remove, }; RTE_INIT(rte_virtio_pmd_init) { rte_eal_iopl_init(); rte_pci_register(&rte_virtio_pmd); } |
|
static int eth_virtio_pci_probe(struct rte_pci_driver *pci_drv __rte_unused, struct rte_pci_device *pci_dev) { if (rte_eal_iopl_init() != 0) { PMD_INIT_LOG(ERR, "IOPL call failed - cannot use virtio PMD"); return 1; } /* virtio pmd skips probe if device needs to work in vdpa mode */ if (vdpa_mode_selected(pci_dev->device.devargs)) return 1; return rte_eth_dev_pci_generic_probe(pci_dev, sizeof(struct virtio_hw),eth_virtio_dev_init); } |
|
/* reset device and renegotiate features if needed */ static int virtio_init_device(struct rte_eth_dev *eth_dev, uint64_t req_features) { struct virtio_hw *hw = eth_dev->data->dev_private; struct virtio_net_config *config; struct virtio_net_config local_config; struct rte_pci_device *pci_dev = NULL; int ret; /* Reset the device although not necessary at startup */ vtpci_reset(hw); if (hw->vqs) { virtio_dev_free_mbufs(eth_dev); virtio_free_queues(hw); } /* Tell the host we've noticed this device. */ vtpci_set_status(hw, VIRTIO_CONFIG_STATUS_ACK); /* Tell the host we've known how to drive the device. */ vtpci_set_status(hw, VIRTIO_CONFIG_STATUS_DRIVER); if (virtio_negotiate_features(hw, req_features) < 0) return -1; if (!hw->virtio_user_dev) { pci_dev = RTE_ETH_DEV_TO_PCI(eth_dev); rte_eth_copy_pci_info(eth_dev, pci_dev); } /* If host does not support both status and MSI-X then disable LSC */ if (vtpci_with_feature(hw, VIRTIO_NET_F_STATUS) && hw->use_msix != VIRTIO_MSIX_NONE) eth_dev->data->dev_flags |= RTE_ETH_DEV_INTR_LSC; else eth_dev->data->dev_flags &= ~RTE_ETH_DEV_INTR_LSC; /* Setting up rx_header size for the device */ if (vtpci_with_feature(hw, VIRTIO_NET_F_MRG_RXBUF) || vtpci_with_feature(hw, VIRTIO_F_VERSION_1)) hw->vtnet_hdr_size = sizeof(struct virtio_net_hdr_mrg_rxbuf); else hw->vtnet_hdr_size = sizeof(struct virtio_net_hdr); /* Copy the permanent MAC address to: virtio_hw */ virtio_get_hwaddr(hw); ether_addr_copy((struct ether_addr *) hw->mac_addr, ð_dev->data->mac_addrs[0]); PMD_INIT_LOG(DEBUG, "PORT MAC: %02X:%02X:%02X:%02X:%02X:%02X", hw->mac_addr[0], hw->mac_addr[1], hw->mac_addr[2], hw->mac_addr[3], hw->mac_addr[4], hw->mac_addr[5]); if (vtpci_with_feature(hw, VIRTIO_NET_F_CTRL_VQ)) { config = &local_config; vtpci_read_dev_config(hw, offsetof(struct virtio_net_config, mac), &config->mac, sizeof(config->mac)); if (vtpci_with_feature(hw, VIRTIO_NET_F_STATUS)) { vtpci_read_dev_config(hw, offsetof(struct virtio_net_config, status), &config->status, sizeof(config->status)); } else { PMD_INIT_LOG(DEBUG, "VIRTIO_NET_F_STATUS is not supported"); config->status = 0; } if (vtpci_with_feature(hw, VIRTIO_NET_F_MQ)) { vtpci_read_dev_config(hw, offsetof(struct virtio_net_config, max_virtqueue_pairs), &config->max_virtqueue_pairs, sizeof(config->max_virtqueue_pairs)); } else { PMD_INIT_LOG(DEBUG, "VIRTIO_NET_F_MQ is not supported"); config->max_virtqueue_pairs = 1; } hw->max_queue_pairs = config->max_virtqueue_pairs; if (vtpci_with_feature(hw, VIRTIO_NET_F_MTU)) { vtpci_read_dev_config(hw, offsetof(struct virtio_net_config, mtu), &config->mtu, sizeof(config->mtu)); /* * MTU value has already been checked at negotiation * time, but check again in case it has changed since * then, which should not happen. */ if (config->mtu < ETHER_MIN_MTU) { PMD_INIT_LOG(ERR, "invalid max MTU value (%u)", config->mtu); return -1; } hw->max_mtu = config->mtu; /* Set initial MTU to maximum one supported by vhost */ eth_dev->data->mtu = config->mtu; } else { hw->max_mtu = VIRTIO_MAX_RX_PKTLEN - ETHER_HDR_LEN - VLAN_TAG_LEN - hw->vtnet_hdr_size; } PMD_INIT_LOG(DEBUG, "config->max_virtqueue_pairs=%d", config->max_virtqueue_pairs); PMD_INIT_LOG(DEBUG, "config->status=%d", config->status); PMD_INIT_LOG(DEBUG, "PORT MAC: %02X:%02X:%02X:%02X:%02X:%02X", config->mac[0], config->mac[1], config->mac[2], config->mac[3], config->mac[4], config->mac[5]); } else { PMD_INIT_LOG(DEBUG, "config->max_virtqueue_pairs=1"); hw->max_queue_pairs = 1; hw->max_mtu = VIRTIO_MAX_RX_PKTLEN - ETHER_HDR_LEN - VLAN_TAG_LEN - hw->vtnet_hdr_size; } ret = virtio_alloc_queues(eth_dev); if (ret < 0) return ret; if (eth_dev->data->dev_conf.intr_conf.rxq) { if (virtio_configure_intr(eth_dev) < 0) { PMD_INIT_LOG(ERR, "failed to configure interrupt"); virtio_free_queues(hw); return -1; } } vtpci_reinit_complete(hw); if (pci_dev) PMD_INIT_LOG(DEBUG, "port %d vendorID=0x%x deviceID=0x%x", eth_dev->data->port_id, pci_dev->id.vendor_id, pci_dev->id.device_id); return 0; } |
在OVS-DPDK中添加一个vhost-user网络接口时:OVS-DPDK会调用rte_vhost_driver_register函数,首先根据传入参数path文件路径创建UNIX domain socket,用于后续virtio-net前端(QEMU虚拟机中的DPDK应用程序)和virtio-net后端(OVS-DPDK应用程序)的通信。
这部分相关的源码在dpdk-stable-18.11.11/lib/librte_vhost/socket.c的第824行,主要的函数是rte_vhost_driver_register。
|
/* * Register a new vhost-user socket; here we could act as server * (the default case), or client (when RTE_VHOST_USER_CLIENT) flag * is set. */ int rte_vhost_driver_register(const char *path, uint64_t flags) { int ret = -1; struct vhost_user_socket *vsocket; if (!path) return -1; pthread_mutex_lock(&vhost_user.mutex); if (vhost_user.vsocket_cnt == MAX_VHOST_SOCKET) { RTE_LOG(ERR, VHOST_CONFIG, "error: the number of vhost sockets reaches maximum "); goto out; } vsocket = malloc(sizeof(struct vhost_user_socket)); if (!vsocket) goto out; memset(vsocket, 0, sizeof(struct vhost_user_socket)); vsocket->path = strdup(path); if (vsocket->path == NULL) { RTE_LOG(ERR, VHOST_CONFIG, "error: failed to copy socket path string "); vhost_user_socket_mem_free(vsocket); goto out; } TAILQ_INIT(&vsocket->conn_list); ret = pthread_mutex_init(&vsocket->conn_mutex, NULL); if (ret) { RTE_LOG(ERR, VHOST_CONFIG, "error: failed to init connection mutex "); goto out_free; } vsocket->vdpa_dev_id = -1; vsocket->dequeue_zero_copy = flags & RTE_VHOST_USER_DEQUEUE_ZERO_COPY; if (vsocket->dequeue_zero_copy && (flags & RTE_VHOST_USER_IOMMU_SUPPORT)) { RTE_LOG(ERR, VHOST_CONFIG, "error: enabling dequeue zero copy and IOMMU features " "simultaneously is not supported "); goto out_mutex; } /* * Set the supported features correctly for the builtin vhost-user * net driver. * * Applications know nothing about features the builtin virtio net * driver (virtio_net.c) supports, thus it's not possible for them * to invoke rte_vhost_driver_set_features(). To workaround it, here * we set it unconditionally. If the application want to implement * another vhost-user driver (say SCSI), it should call the * rte_vhost_driver_set_features(), which will overwrite following * two values. */ vsocket->use_builtin_virtio_net = true; vsocket->supported_features = VIRTIO_NET_SUPPORTED_FEATURES; vsocket->features = VIRTIO_NET_SUPPORTED_FEATURES; vsocket->protocol_features = VHOST_USER_PROTOCOL_FEATURES; /* * Dequeue zero copy can't assure descriptors returned in order. * Also, it requires that the guest memory is populated, which is * not compatible with postcopy. */ if (vsocket->dequeue_zero_copy) { if ((flags & RTE_VHOST_USER_CLIENT) != 0) RTE_LOG(WARNING, VHOST_CONFIG, "zero copy may be incompatible with vhost client mode "); vsocket->supported_features &= ~(1ULL << VIRTIO_F_IN_ORDER); vsocket->features &= ~(1ULL << VIRTIO_F_IN_ORDER); RTE_LOG(INFO, VHOST_CONFIG, "Dequeue zero copy requested, disabling postcopy support "); vsocket->protocol_features &= ~(1ULL << VHOST_USER_PROTOCOL_F_PAGEFAULT); } if (!(flags & RTE_VHOST_USER_IOMMU_SUPPORT)) { vsocket->supported_features &= ~(1ULL << VIRTIO_F_IOMMU_PLATFORM); vsocket->features &= ~(1ULL << VIRTIO_F_IOMMU_PLATFORM); } if (!(flags & RTE_VHOST_USER_POSTCOPY_SUPPORT)) { vsocket->protocol_features &= ~(1ULL << VHOST_USER_PROTOCOL_F_PAGEFAULT); } else { } if ((flags & RTE_VHOST_USER_CLIENT) != 0) { vsocket->reconnect = !(flags & RTE_VHOST_USER_NO_RECONNECT); if (vsocket->reconnect && reconn_tid == 0) { if (vhost_user_reconnect_init() != 0) goto out_mutex; } } else { vsocket->is_server = true; } ret = create_unix_socket(vsocket); if (ret < 0) { goto out_mutex; } vhost_user.vsockets[vhost_user.vsocket_cnt++] = vsocket; pthread_mutex_unlock(&vhost_user.mutex); return ret; } |
发送数据处理过程
vhost-user前端:在vhost-user接口创建之后,会调用rte_vhost_driver_start函数:首先根据UNIX domain socket的文件路径path找到对应的socket,然后会调用函数创建监听线程,
这个线程的处理函数是fdset_event_dispatch会去监听vhost_user.fdset指定的socket fd的读写操作,进而实现和vhost-user后端的通信。这部分的实现代码在:dpdk-stable-18.11.11/lib/librte_vhost/socket.c的第1094行。
|
int rte_vhost_driver_start(const char *path) { struct vhost_user_socket *vsocket; static pthread_t fdset_tid; pthread_mutex_lock(&vhost_user.mutex); vsocket = find_vhost_user_socket(path); pthread_mutex_unlock(&vhost_user.mutex); if (!vsocket) return -1; if (fdset_tid == 0) { /** * create a pipe which will be waited by poll and notified to * rebuild the wait list of poll. */ if (fdset_pipe_init(&vhost_user.fdset) < 0) { RTE_LOG(ERR, VHOST_CONFIG, "failed to create pipe for vhost fdset "); return -1; } int ret = rte_ctrl_thread_create(&fdset_tid, "vhost-events", NULL, fdset_event_dispatch, &vhost_user.fdset); if (ret != 0) { RTE_LOG(ERR, VHOST_CONFIG, "failed to create fdset handling thread"); fdset_pipe_uninit(&vhost_user.fdset); return -1; } } if (vsocket->is_server) return vhost_user_start_server(vsocket); else return vhost_user_start_client(vsocket); } |
vhost-user后端:当vhost-user前端(QEMU虚拟机的DPDK应用程序)向UNIX domain socket写入事件的时候,之前所说的那个监听线程会捕获到这个事件,调用vhost_user_read_cb函数进行处理,最终会调用vhost_user_msg_handler函数,根据不同的消息类型做不同的处理。
这部分的实现代码在:dpdk-stable-18.11.11/lib/librte_vhost/socket.c的第293行。
|
static void vhost_user_read_cb(int connfd, void *dat, int *remove) { struct vhost_user_connection *conn = dat; struct vhost_user_socket *vsocket = conn->vsocket; int ret; ret = vhost_user_msg_handler(conn->vid, connfd); if (ret < 0) { struct virtio_net *dev = get_device(conn->vid); close(connfd); *remove = 1; if (dev) vhost_destroy_device_notify(dev); if (vsocket->notify_ops->destroy_connection) vsocket->notify_ops->destroy_connection(conn->vid); vhost_destroy_device(conn->vid); if (vsocket->reconnect) { create_unix_socket(vsocket); vhost_user_start_client(vsocket); } pthread_mutex_lock(&vsocket->conn_mutex); TAILQ_REMOVE(&vsocket->conn_list, conn, next); pthread_mutex_unlock(&vsocket->conn_mutex); free(conn); } } |
收发数据包的函数分别是eth_vhost_rx和eth_vhost_tx。代码的具体实现在dpdk-stable-18.11.11/drivers/net/vhost/rte_eth_vhost.c中。
函数eth_dev_vhost_create用来创建vhost-user的后端设备的时候,会注册发送和接收数据的回调函数为eth_vhost_rx和eth_vhost_tx。
在DPDK中,发送和接收数据包的代码都是在DPDK中实现的,代码的可读性比较好。只是特别要注意的是同样的DPDK代码,运行的位置不一样:前端是在QEMU虚拟机中运行的DPDK应用程序,后端运行在OVS-DPDK中。
|
static int eth_dev_vhost_create(struct rte_vdev_device *dev, char *iface_name, int16_t queues, const unsigned int numa_node, uint64_t flags) { const char *name = rte_vdev_device_name(dev); struct rte_eth_dev_data *data; struct pmd_internal *internal = NULL; struct rte_eth_dev *eth_dev = NULL; struct ether_addr *eth_addr = NULL; struct rte_vhost_vring_state *vring_state = NULL; struct internal_list *list = NULL; VHOST_LOG(INFO, "Creating VHOST-USER backend on numa socket %u ", numa_node); list = rte_zmalloc_socket(name, sizeof(*list), 0, numa_node); if (list == NULL) goto error; /* reserve an ethdev entry */ eth_dev = rte_eth_vdev_allocate(dev, sizeof(*internal)); if (eth_dev == NULL) goto error; data = eth_dev->data; eth_addr = rte_zmalloc_socket(name, sizeof(*eth_addr), 0, numa_node); if (eth_addr == NULL) goto error; data->mac_addrs = eth_addr; *eth_addr = base_eth_addr; eth_addr->addr_bytes[5] = eth_dev->data->port_id; vring_state = rte_zmalloc_socket(name, sizeof(*vring_state), 0, numa_node); if (vring_state == NULL) goto error; /* now put it all together * - store queue data in internal, * - point eth_dev_data to internals * - and point eth_dev structure to new eth_dev_data structure */ internal = eth_dev->data->dev_private; internal->dev_name = strdup(name); if (internal->dev_name == NULL) goto error; internal->iface_name = rte_malloc_socket(name, strlen(iface_name) + 1, 0, numa_node); if (internal->iface_name == NULL) goto error; strcpy(internal->iface_name, iface_name); list->eth_dev = eth_dev; pthread_mutex_lock(&internal_list_lock); TAILQ_INSERT_TAIL(&internal_list, list, next); pthread_mutex_unlock(&internal_list_lock); rte_spinlock_init(&vring_state->lock); vring_states[eth_dev->data->port_id] = vring_state; data->nb_rx_queues = queues; data->nb_tx_queues = queues; internal->max_queues = queues; internal->vid = -1; data->dev_link = pmd_link; data->dev_flags = RTE_ETH_DEV_INTR_LSC; eth_dev->dev_ops = &ops; /* finally assign rx and tx ops */ eth_dev->rx_pkt_burst = eth_vhost_rx; eth_dev->tx_pkt_burst = eth_vhost_tx; if (rte_vhost_driver_register(iface_name, flags)) goto error; if (rte_vhost_driver_callback_register(iface_name, &vhost_ops) < 0) { VHOST_LOG(ERR, "Can't register callbacks "); goto error; } if (rte_vhost_driver_start(iface_name) < 0) { VHOST_LOG(ERR, "Failed to start driver for %s ", iface_name); goto error; } rte_eth_dev_probing_finish(eth_dev); return 0; error: if (internal) { rte_free(internal->iface_name); free(internal->dev_name); } rte_free(vring_state); rte_eth_dev_release_port(eth_dev); rte_free(list); return -1; } |
02
vDPA
DPDK场景下的vhost-user是virtio-net在用户态的实现。和内核的实现相比,提高了网络数据的处理能力。但毕竟还是纯软件层面的实现,在性能上肯定比不过硬件层面的实现。
为了进一步提升性能,Intel还推出了vDPA (vHost Data Path Acceleration) 的硬件解决方案,直接让网卡与虚拟机内的virtio虚拟队列交互,把数据包DMA到虚拟机的缓存内,在支持了virtio标准的基础上实现了真正意义上的零拷贝。
在DPDK 18.05之后的版本中,已经开始支持vDPA的特性了。vDPA这部分的实现主要是在网卡中,相当于把virtio后端实现在网卡中了。
所以,我们这里只关注一下virtio前端和vDPA设备之间的关联。这部分实现的相关代码在dpdk-stable-18.11.11/examples/vdpa/main.c,第143行start_vdpa函数中的rte_vhost_driver_attach_vdpa_device函数中实现了vhost-user的vsocket数据结构和vDPA设备ID的关联。
|
static int start_vdpa(struct vdpa_port *vport) { int ret; char *socket_path = vport->ifname; int did = vport->did; if (client_mode) vport->flags |= RTE_VHOST_USER_CLIENT; if (access(socket_path, F_OK) != -1 && !client_mode) { RTE_LOG(ERR, VDPA, "%s exists, please remove it or specify another file and try again. ", socket_path); return -1; } ret = rte_vhost_driver_register(socket_path, vport->flags); if (ret != 0) rte_exit(EXIT_FAILURE, "register driver failed: %s ", socket_path); ret = rte_vhost_driver_callback_register(socket_path, &vdpa_sample_devops); if (ret != 0) rte_exit(EXIT_FAILURE, "register driver ops failed: %s ", socket_path); ret = rte_vhost_driver_attach_vdpa_device(socket_path, did); if (ret != 0) rte_exit(EXIT_FAILURE, "attach vdpa device failed: %s ", socket_path); if (rte_vhost_driver_start(socket_path) < 0) rte_exit(EXIT_FAILURE, "start vhost driver failed: %s ", socket_path); return 0; } |
|
int rte_vhost_driver_attach_vdpa_device(const char *path, int did) { struct vhost_user_socket *vsocket; if (rte_vdpa_get_device(did) == NULL || path == NULL) return -1; pthread_mutex_lock(&vhost_user.mutex); vsocket = find_vhost_user_socket(path); if (vsocket) vsocket->vdpa_dev_id = did; pthread_mutex_unlock(&vhost_user.mutex); return vsocket ? 0 : -1; } |
原文标题:virtio技术的演进和发展 (2/2)
文章出处:【微信公众号:Linux阅码场】欢迎添加关注!文章转载请注明出处。
责任编辑:haq
-
请问LS1012的DPDK怎么配置呢2022-01-05 0
-
ovs-dpdk sgmii口不能正常转发是为什么2022-01-05 0
-
Arm上带DPDK的Open vSwitch测试系列2022-03-31 0
-
DPDK安装教程和DPDK程序运行收发包示例程序及性能对比实验的详细概述2018-09-03 1162
-
建立和运行DPDK,使用英特尔QuickAssist设备加密2018-10-17 2270
-
用DPDK启动VCwitter并配置端口2018-09-11 3424
-
DPDK和Virtio的简介2018-10-30 4628
-
DPDK的设计方法与API应用介绍2018-10-30 3934
-
如何为您的NFV应用设置DPDK2018-11-12 3009
-
DPDK开源社区更新2018-11-13 4258
-
DPDK API和虚拟基础架构2018-11-08 3874
-
使用DPDK打开VSwitch:架构和性能2018-11-08 3501
-
DPDK内存的基本概念2020-10-26 2091
-
简述高速流量处理DPDK替代方案2021-06-22 2737
-
龙芯自主CPU指令系统获得开源DPDK支持2022-12-08 1369
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

