

使用OpenHarmony专用开发工具开发变频器控制界面
描述
在工农业生产中,变频器有着广泛和深远的应用,变频器的控制除了本地操作面板和按钮,旋钮控制外,更多是通过上位机来进行远程操作和监控。
2022 年 3 月 30 日,OpenHarmony 3.1 Release 及配套南向开发工具 DevEco Device Tool 3.0 Release 发布。
3 月 31 日发布了 OpenHarmony 首款北向应用开发工具 DevEco Studio 3.0 Beta3 for OpenHarmony,支持 API 8 和 API 9。
具有以下能力特点:
-
支持一站式的信息获取平台
-
支持可视化的界面 UI 开发
-
双向、极速的 UI 预览
-
全新的编译工具 Hvigor,实现 OpenHarmony 应用/服务的一键自动化构建。
-
支持全自动化的应用签名机制,一键生成签名信息,签名过的 HAP 可以安装到真实设备上运行
-
高效的代码编辑,提供代码高亮、代码折叠、代码格式化等各种常用技巧,同时支持联想补齐、代码跳转、代码校验等,实现代码的高效编辑。
-
预览器支持双向、极速UI预览,实现了应用开发过程的可视化。
-
丰富的代码调试调优能力
让我们用 DevEco Studio 3.0 Beta3 for OpenHarmony,开发一个变频器控制的界面,实现常见的启停,正反转,加减速功能。
模拟器效果如下:

预备
①Hi3516 开发板,烧录好 OpenHarmony 3.1 Release 标准系统
参考 1:
https://ost.51cto.com/posts/10969
参考 2:
https://ost.51cto.com/posts/11038
②安装 OpenHarmony 专用开发工具 DevEco Studio 3.0 Beta3 for OpenHarmony
官网文档:
https://developer.harmonyos.com/cn/docs/documentation/doc-guides/ohos-download-software-0000001218760592
创建工程
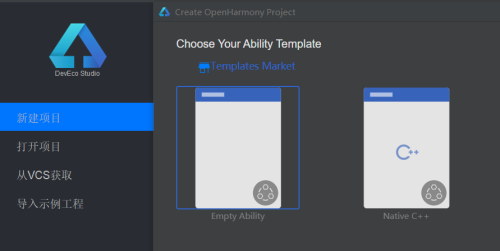
①打开应用,点击新建项目,弹窗选择“Empty Ability”后点击"Next"
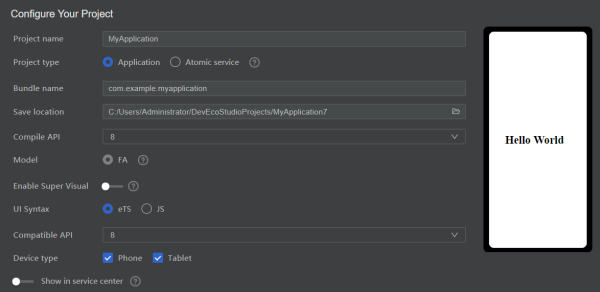
②弹出的工程配置里全部默认,点击“finish”完成 eTS 工程创建。
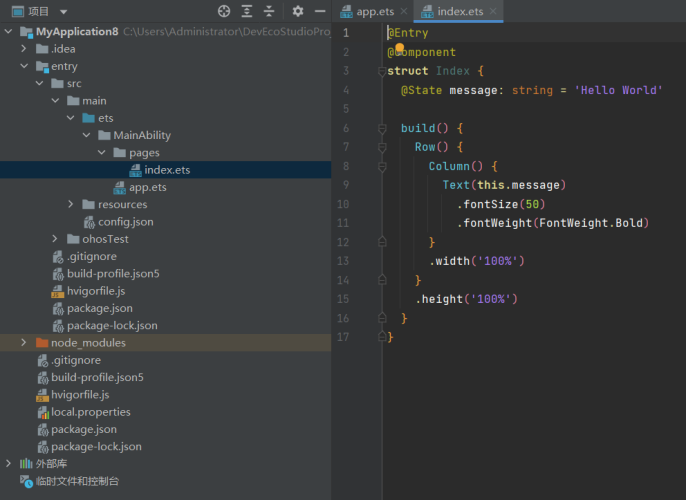
③工程结构
如下:
-
index.ets:用于描述 UI 布局、样式、事件交互和页面逻辑。
-
app.ets:用于全局应用逻辑和应用生命周期管理。
-
pages:用于存放所有组件页面。
- resources:用于存放资源配置文件。
图片,代码,自动签名,联机调试
将工程中使用到的图片,添加到 resources -> base -> media 目录下:
①编辑代码,打开预览器的双 T,可以实时双向预览。
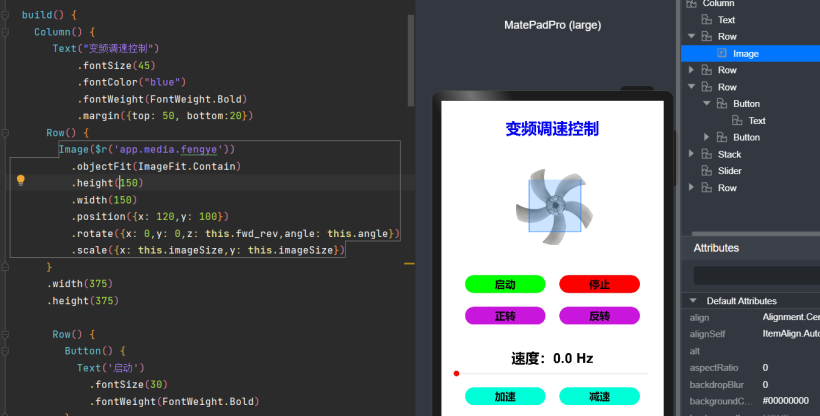
②完整代码在 codelabs 的 SliderApplicationEts 基础上修改而成:
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
@State private speed: number = 0
@State private lastspeed: number = 1
@State private imageSize: number = 1.5
@State private fwd_rev: number = 1
@State private angle: number = 0
@State private interval: number = 0
build() {
Column() {
Text("变频调速控制")
.fontSize(45)
.fontColor("blue")
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.margin({top: 50, bottom:20})
Row() {
Image($r('app.media.fengye'))
.objectFit(ImageFit.Contain)
.height(150)
.width(150)
.position({x: 120,y: 100})
.rotate({x: 0,y: 0,z: this.fwd_rev,angle: this.angle})
.scale({x: this.imageSize,y: this.imageSize})
}
.width(375)
.height(375)
Row() {
Button() {
Text('启动')
.fontSize(30)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
}
.type(ButtonType.Capsule)
.margin({ left: 20 ,right: 20 })
.width('40%')
.height('5%')
.backgroundColor('green')
.onClick(() => {
this.speed = this.lastspeed
})
Button() {
Text('停止')
.fontSize(30)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
}
.type(ButtonType.Capsule)
.margin({ left: 20 ,right: 20 })
.width('40%')
.height('5%')
.backgroundColor('red')
.onClick(() => {
this.speed = 0
})
}
Row() {
Button() {
Text('正转')
.fontSize(30)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
}
.type(ButtonType.Capsule)
.margin({ top: 40,left: 20 ,right: 20 })
.width('40%')
.height('5%')
.backgroundColor('#ffc916dd')
.onClick(() => {
this.fwd_rev = 1
})
Button() {
Text('反转')
.fontSize(30)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
}
.type(ButtonType.Capsule)
.margin({ top: 40,left: 20 ,right: 20 })
.width('40%')
.height('5%')
.backgroundColor('#ffc916dd')
.onClick(() => {
this.fwd_rev = -1
})
}
this.DescribeText('速度:',this.speed * 5)
Slider({value: this.speed, min: 0, max: 10,step: 0.2,style:SliderStyle.OutSet})
.showTips(true)
.blockColor(Color.Red)
.onChange((value: number,mode:SliderChangeMode) => {
this.speed = value
this.lastspeed = this.speed
clearInterval(this.interval)
this.speedChange()
})
Row() {
Button() {
Text('加速')
.fontSize(30)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
}
.type(ButtonType.Capsule)
.margin({ top: 20,left: 20 ,right: 20 })
.width('40%')
.height('5%')
.backgroundColor('#ff00ffd9')
.onClick(() => {
this.speed += 0.2
if (this.speed >= 10) {
this.speed = 10
}
this.lastspeed = this.speed
})
Button() {
Text('减速')
.fontSize(30)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
}
.type(ButtonType.Capsule)
.margin({ top: 20,left: 20 ,right: 20 })
.width('40%')
.height('5%')
.backgroundColor('#ff00ffd9')
.onClick(() => {
this.speed -= 0.2
if (this.speed <= 0) {
this.speed = 0
}
this.lastspeed = this.speed
})
}
}
.margin({left: 30,right: 30})
}
speedChange() {
var that = this;
that.angle = 0;
this.interval = setInterval(function () {
that.angle += that.speed
}, 15)
}
onPageShow() {
clearInterval(this.interval)
this.speedChange()
}
@Builder DescribeText(text:string, speed: number) {
Stack() {
Text(text + speed.toFixed(1) + ' Hz')
.margin({ top: 70 })
.fontSize(40)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
}
}
}
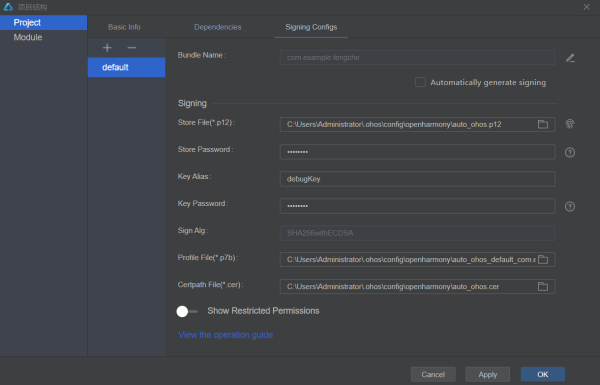
③连接真实设备前,IDE 提供了自动化签名功能。依次点击“文件——项目结构——Project——Signing Config",弹窗中勾选“Automatically generate signing”后,等待签名完成,点击“ok”。
 ⑤点击设备“运行”按钮,同时完成工程编译和下载到开发板。
⑤点击设备“运行”按钮,同时完成工程编译和下载到开发板。
效果如下:
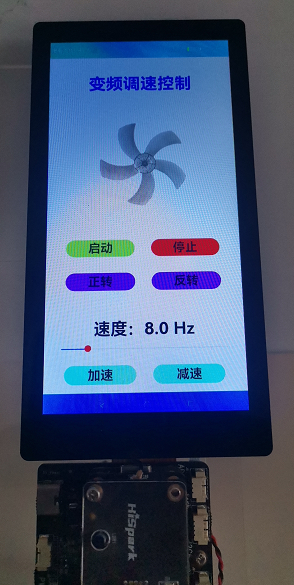 OpenHarmony 已经建立了完整的开发工具链,它的生态会越来越强大。
OpenHarmony 已经建立了完整的开发工具链,它的生态会越来越强大。
原文标题:开源鸿蒙首款IDE开发OpenHarmony 3.1应用
文章出处:【微信公众号:HarmonyOS技术社区】欢迎添加关注!文章转载请注明出处。
- 相关推荐
- 变频器
- 开发工具
- OpenHarmony
-
STM32 VR开发工具2017-02-17 960
-
OpenHarmony 设备开发工具简介2021-06-08 0
-
Andioid开发环境和开发工具2017-05-05 1885
-
光伏水泵专用变频器规格书2017-09-21 796
-
双变频拉丝机专用变频器说明书2017-09-21 875
-
STM32系列微控制器开发工具与应用2017-09-29 848
-
ARM开发工具解读2017-10-18 1090
-
web前端开发工具排行:8款html开发工具推荐下载2018-02-01 85231
-
变频器专用输出电抗器的介绍2021-12-16 4538
-
OpenHarmony开发者大会 开发工具分william hill官网 :聚能量赢未来,工具助力应用创新2023-05-08 1308
-
常用的上位机开发工具2023-05-09 1291
-
Intellij IDEA 开发工具实例2023-09-25 905
-
开发板和开发工具指南2023-10-26 633
-
图形界面开发工具GUI Guider的使用教程2023-12-20 19422
-
矢量专用变频器和通用变频器的区别2024-02-04 2245
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

