

ESP32学习笔记:NVS分区永久保存数据
描述
今天我们来说说ESP32 for Arduino NVS分区永久保存数据。
ESP32 for Arduino NVS分区
上一节我们讲了整个ESP32的存储分布,其中有一个NVS分区,这个分区专门用来存储数据的,系统在复位或断电后数据仍然存在,我们可以使用Preferences库保存网络SSID,密码,一些阈值或者IO的最后状态等。
在保存数据的时候,我们推荐使用Preferences库,不推荐使用EEPROM库。
使用Preferences库保存的数据结构如下,也叫键值对:
namespace {
key:value
}
一个命名空间中也可以有不同的键:
namespace {
key1: value1
key2: value2
}
实际使用中,我们可以用来保存网络凭证:
credentials {
ssid: "your_ssid"
pass: "your_pass"
}
也可以有多个具有相同键的命名空间(但每个键都有其值):
namespace1{
key:value1
}
namespace2{
key:value2
}
使用Preferences库时,应该定义要保存的数据类型。如果想读取该数据,则必须知道保存的数据类型,也就是说,写入和读取的数据类型应该相同。
支持以下数据类型的保存:char、char、short、Ushort、int、Uint、long、Ulong、long64、Ulong64、float、double、bool、字符串和字节。
Preferences库函数说明
首先包含头文件
Preferences 库
然后定义一个实例
Preferences preferences;
打开一个命名空间
begin方法打开一个带有定义命名空间的“储存空间”,参数为false代表我们在读/写模式下使用,为true代表以只读的方式打开或创建命令空间,命名空间名称最多为15个字符。
preferences.begin("my-app", false);
清除preferences
从打开的命名空间中删除一个键。
preferences.remove(key);
关闭preferences
使用end方法在打开的命名空间下关闭preferences
preferences.end();
放置一个k-v
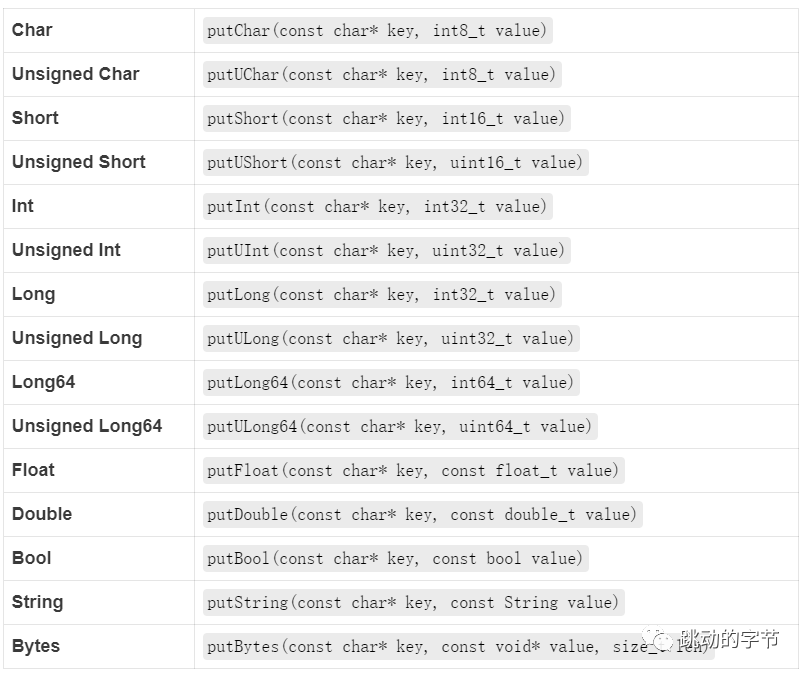
获取一个k-v

删除命名空间
在Preferences 库中,并没有完全删除命令空间的方法,我们存储很多数据之后,nvs分区可能就满了,所以我们想要完全擦除nvs分区,可以使用以下程序运行一次:
#include < nvs_flash.h >
void setup() {
nvs_flash_erase(); // 擦除NVS分区
nvs_flash_init(); // 初始化NVS分区
while(true);
}
void loop() {
}
程序示例
我们直接打开Example中的例子,StartCounter
/*
ESP32 startup counter example with Preferences library.
This simple example demonstrates using the Preferences library to store how many times the ESP32 module has booted.
The Preferences library is a wrapper around the Non-volatile storage on ESP32 processor.
created for arduino-esp32 09 Feb 2017 by Martin Sloup (Arcao)
Complete project details at https://RandomNerdTutorials.com/esp32-save-data-permanently-preferences/
*/
#include < Preferences.h >
Preferences preferences;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println();
// Open Preferences with my-app namespace. Each application module, library, etc
// has to use a namespace name to prevent key name collisions. We will open storage in
// RW-mode (second parameter has to be false).
// Note: Namespace name is limited to 15 chars.
preferences.begin("my-app", false);
// Remove all preferences under the opened namespace
//preferences.clear();
// Or remove the counter key only
//preferences.remove("counter");
// Get the counter value, if the key does not exist, return a default value of 0
// Note: Key name is limited to 15 chars.
unsigned int counter = preferences.getUInt("counter", 0);
// Increase counter by 1
counter++;
// Print the counter to Serial Monitor
Serial.printf("Current counter value: %un", counter);
// Store the counter to the Preferences
preferences.putUInt("counter", counter);
// Close the Preferences
preferences.end();
// Wait 10 seconds
Serial.println("Restarting in 10 seconds...");
delay(10000);
// Restart ESP
ESP.restart();
}
void loop() {
}
这个例子增加了一个counter键,每次运行都加一,我们在按下复位键之后,可以看到下面你的现象,数据保存起来了。
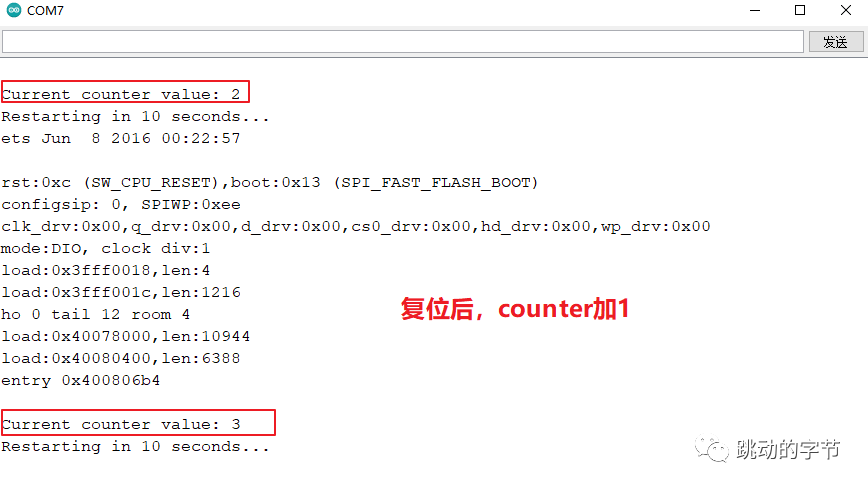
Preferences库很方便保存键:值对。即使在重置 ESP32 或断电后,闪存中保存的数据仍然存在。
感谢大家,关于ESP32的学习,希望大家Enjoy!
-
请问esp32s3如何保存突然停电时的数据?2024-06-06 0
-
ESP32-S3-WROMM-1U同时读取nvs和写ota分区会造成系统异常吗?2024-06-07 0
-
ESP32-S3无法使用NVS分区是怎么回事?2024-06-18 0
-
基于PlatfromIO-Arduino的ESP32-Flash分区2022-01-26 0
-
ESP32之ESP-IDF学习笔记2022-02-22 0
-
使用ESP32-S3无法使用NVS分区是为什么?2023-02-15 0
-
如何将ESP-IDF引导加载程序与用于NVS的ESP32-Arduino代码一起使用?2023-04-13 0
-
ESP32 开发笔记(四)LVGL控件学习 Window 窗口控件 X2021-11-14 1060
-
ESP32驱动AD77052021-11-23 776
-
ESP32-Flash分区,基于PlatfromIO-Arduino2021-12-02 856
-
[ESP8266学习笔记]components_nvs 非易失性存储 Non-Volatile Storage(NVS),保存数据到flash2021-12-02 1200
-
[ESP32]学习笔记022021-12-03 823
-
[ESP32]学习笔记042021-12-22 777
-
SPI主线协议——ESP32学习笔记2021-12-22 771
-
ESP32学习笔记:WiFi2023-07-15 3935
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

