

考虑x和z在verilog条件语句中的使用情况
描述
首先,考虑x和z在verilog条件语句中的使用情况,然后我们再考虑在verilog中用x和z给其他reg/wire赋值的情况。
(一)首先,考虑x和z在verilog条件语句中的使用情况。
Verilog case语句中,2'b1x和2’b0x造成的仿真器、综合器的mismatch,
举个例子:
Simulators:
match 2'b1x to 11 or 10
match 2’b0x to 01 or 00
HDL Compiler tool
both 2'b1x and 2’b0x are evaluated to false. Because of the simulation and synthesis mismatches, the HDL Compiler tool issues an ELAB-310 warning.
case (A) 2'b1x:... // You want 2'b1x to match 11 and 10 but // HDL Compiler always evaluates this comparison to false 2'b0x:... // you want 2'b0x to match 00 and 01 but // HDL Compiler always evaluates this comparison to false default: ... endcase
官方说明:我们可以得到两点信息:

第一点:
A simulator evaluates an unknown (x) or high impedance (z) as a distinct value different from 0 or 1; however, an x or z value becomes a 0 or 1 during synthesis.
第二点:
DC工具会直接将verilog比较判断语句中的x or z直接理解为false。所以禁止在verilog比较判断语句中使用x or z。
参见如下代码,DC工具会理解 if (A==1'bx) 为false, 因此DC会直接assigns 1 to reg B 并且报 ELAB-310 warning.
module test ( input A, output reg B ); always @(*) begin if(A == 1'bx) B = 0; else B = 1; end endmodule
实际综合如下,果不其然,有意思哇!后面几个稍微复杂点的代码更有趣!
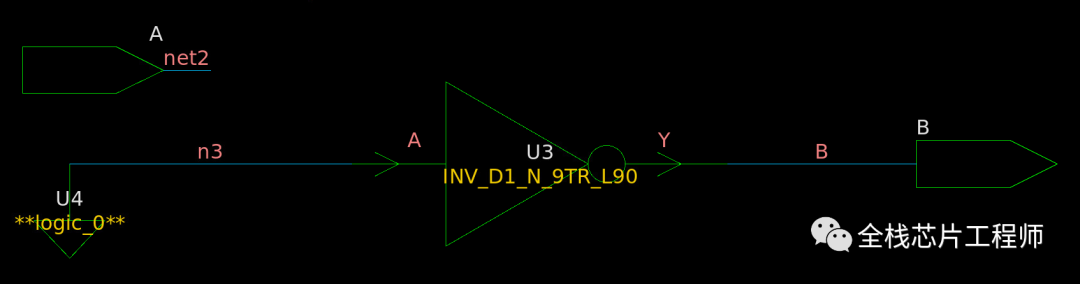
再补充z的使用:
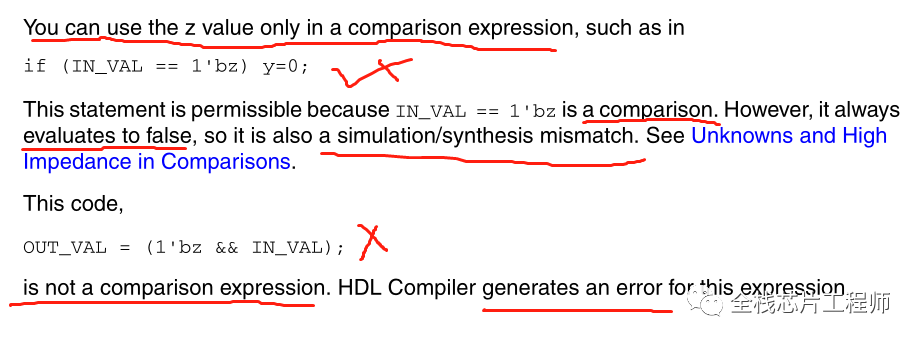
结论:仿真工具可以理解x、z、0、1状态,但是综合工具遇到带x、z的比较判断条件时,直接理解该条件为false。
(二)然后我们再考虑在verilog中用x和z给其他reg/wire赋值的情况。
案例1:z赋值是没问题的,会综合出来三态门,参见如下代码1:
module three_state (ENABLE, IN1, OUT1); input IN1, ENABLE; output reg OUT1; always @(ENABLE or IN1) begin if (ENABLE) OUT1 = IN1; else OUT1 = 1'bz; //assigns high-impedance state end endmodule
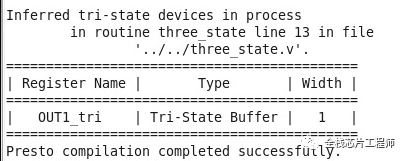
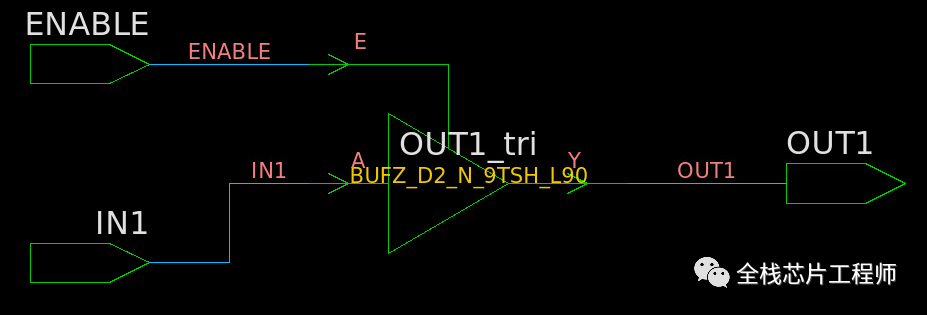
Logical buffer of a single input with an active-high output enable. The output is 3-stated when the enable is low.
真值表:
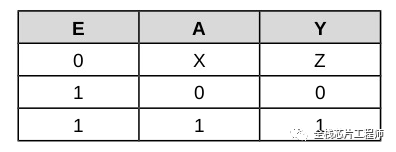
案例2:z赋值是没问题的,会综合出来三态门,参见如下代码2:
module x_state (IN1, OUT1); input [1:0] IN1 ; output reg [1:0] OUT1; always @(*) begin case(IN1) 2'b00 : OUT1 = 2'b00; 2'b01 : OUT1 = 2'b01; 2'b10 : OUT1 = 2'b10; default : OUT1 = 2'bzz; //assigns high-impedance state endcase end endmodule
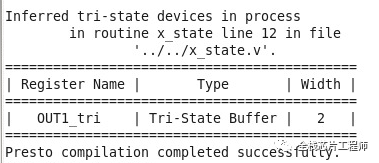
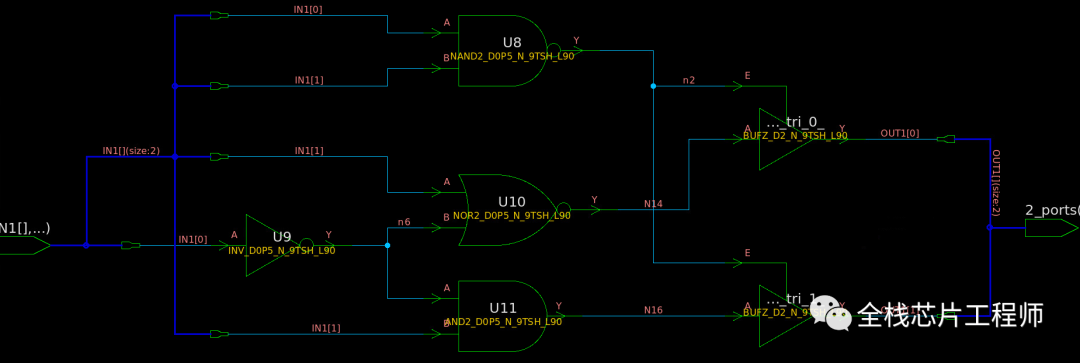
再看X赋值是什么情况。
案例1:利用DC综合工具实测如下代码综合效果:
module x_state (IN1, OUT1); input [1:0] IN1 ; output reg [1:0] OUT1; always @(*) begin case(IN1) 2'b00 : OUT1 = 2'b01; 2'b11 : OUT1 = 2'b00; default : OUT1 = 2'bxx; endcase end endmodule
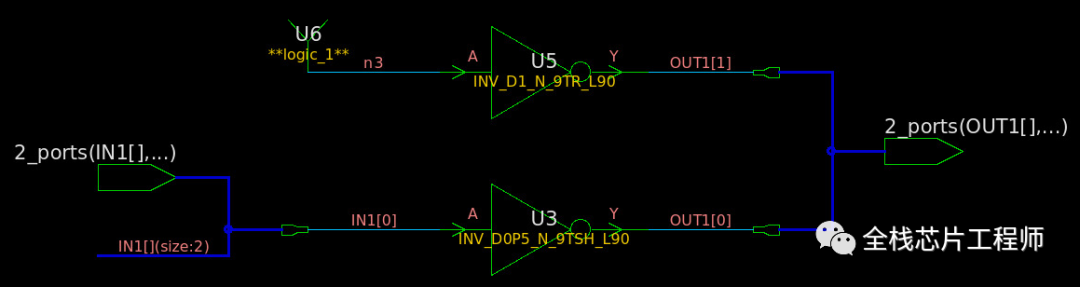
可见,x赋值直接被DC工具省略,也没有latch出现。
案例2:
module x_state (IN1, OUT1); input [1:0] IN1 ; output reg [1:0] OUT1; always @(*) begin case(IN1) 2'b00 : OUT1 = 2'b00; 2'b01 : OUT1 = 2'b01; 2'b10 : OUT1 = 2'b10; default : OUT1 = 2'bxx; //assigns high-impedance state endcase end endmodule
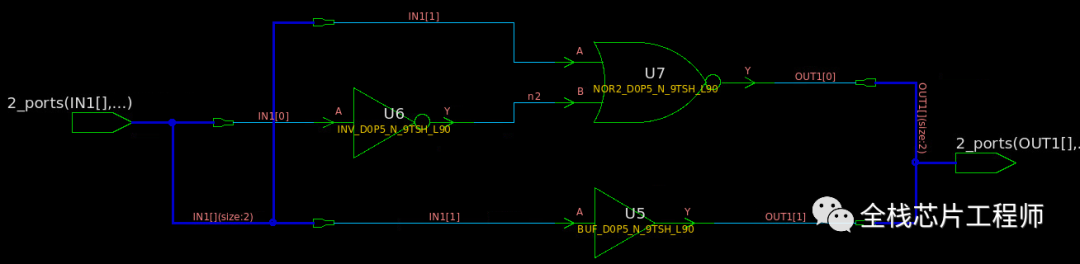
可见,x赋值直接被DC工具省略,也没有latch出现。
案例3:注释掉default,非full_case,必然出现latch!
module x_state (IN1, OUT1); input [1:0] IN1 ; output reg [1:0] OUT1; always @(*) begin case(IN1) 2'b00 : OUT1 = 2'b00; 2'b01 : OUT1 = 2'b01; 2'b10 : OUT1 = 2'b10; endcase end endmodule
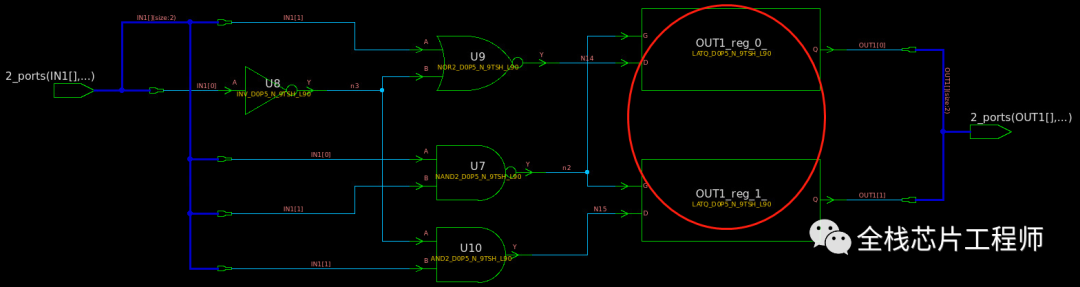
因此,尽管x赋值直接被DC工具省略,也没有latch出现,但是仍然建议不要使用x赋值,除非full_case情况下,不会执行default条件下的x赋值分支,写x赋值可以用于仿真查看波形,如下代码所示:
always @(*)begin case(pmu_state) // During power down sequence, shifting pattern to active // ISOLATE -> RETAIN -> PWRDOWN // and stay unchange during powered down state `ARM_POWERING_DOWN, `ARM_POWERED_DOWN: begin nxt_isolate_n = 1'b0; nxt_retain_n = ISOLATEn; nxt_pwrdown = ~RETAINn; end // During power up sequence, shifting pattern to active // PWRDOWN -> RETAIN -> ISOLATE `ARM_POWERING_UP, `ARM_POWERED_UP: begin nxt_pwrdown = 1'b0 ; nxt_retain_n = ~PWRDOWN ; nxt_isolate_n = RETAINn ; end // Propagate X default: begin nxt_isolate_n = 1'bX; nxt_retain_n = 1'bX; nxt_pwrdown = 1'bX; end endcase end
审核编辑:汤梓红
-
CUBEIDE运行完可以看RAM的使用情况,运行中可以实时查看RAM的使用情况吗?2024-03-12 0
-
如何查看RAM使用情况?2019-08-05 0
-
Android应用的内存使用情况检查方法2020-03-30 0
-
电池使用情况统计信息2021-12-31 0
-
如何检查imx6中的GPU使用情况?2023-05-22 0
-
SoC如何查看内存使用情况2023-09-19 0
-
主流GPS芯片使用情况2017-11-27 3706
-
在Linux系统下使用top命令查看CPU使用情况2020-07-10 4404
-
STM32/KEIL/MDK 查看 FLASH 和 RAM 使用情况2021-12-02 1028
-
SAS运算符in在宏语句中的应用2023-05-19 2292
-
LPC86x上的开关矩阵使用情况2023-08-17 240
-
LPC86x ACMP使用情况2023-08-17 279
-
LPC86x ADC使用情况2023-08-16 239
-
python if语句多个条件怎么用2023-11-21 3044
-
TMS320C64x在高性能DSP应用中的高速缓存使用情况2024-10-21 88
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

