

Formal Verification (二) FPV、APPs介绍
电子说
描述
SVA in Formal
FPV对不同的SVA Property,调用合适的算法engine进行建模,依据算法模型从初始状态Reset state对DUT所有的input自动施加激励,随着cycle的depth增加,逐渐穷尽状态空间。
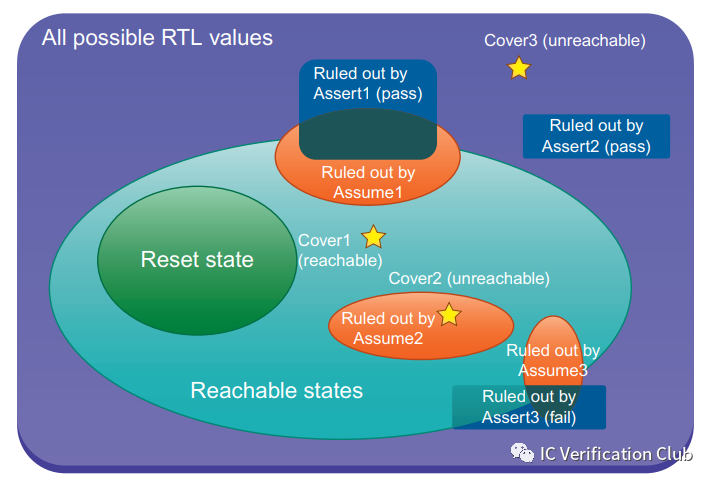
The full space of all possible RTL state values: 最外层的紫方框为RTL的所有可能存在的状态空间(input + state element(dff,latch))。
The reset states:初始状态,一般从reset复位开始。
The reachable states:从reset state可以,自动对input施加激励,可以达到的状态。(所以紫方框以内绿椭圆以外的空间,是无法达到的空间,例如RTL中的dead code) Assumptions:使用SVA的assume对DUT进行约束;橙色椭圆型,约束缩小了状态空间。
Assertion: 使用SVA的assert对property进行断言;断言属性定义了模型的行为,例如assert property: ( @(posedge clk) clr |=> ((overfloat==0)&&(cnt==0))); 断言了在clk上升沿采样时,若clr为高(先行算子anteceden成功),下一个clk上升沿采样到的overfloat和cnt都为0(后续算子consequent);而Formal工具要做的就是穷尽状态空间找出一个counter-example CEX反例,进行falsified证伪,例如overfloat和cnt都不为0或者只有一个为0;如果CEX出现,而assertion为golden,则就说明DUT不满足spec。
Asser1: pass,因为这个CEX不满足assumptions的约束,不是一个有效状态。
Assert2: pass,因为这个CEX本身不是可以达到的状态。
Assert3: fail,有效状态和约束内,出现了一个CEX。
Cover Points: 使用SVA的cover对property设置覆盖点;相当于设置一个观察点,Formal工具会穷尽状态空间,找到一个满足要求的状态;
Cover1: 该覆盖点被cover
Cover2: 该覆盖点在约束之外,unreachable
Cover3: 该覆盖点在有效空间之外,unreachable
VC Formal定义了Assertion和Cover Points的结果如下:
Assertion: proven: assertion pass,穷尽状态空间也找不到一个CEX falsified:assertion fail,出现不满足断言的CEX inconclusive: Formal在N个cycle depth内,没有找到CEX,属于Bounded Proof,有界证明,这个"界“bounded (safe) depth就是N个cycle depth。 vacuous:对于包含蕴含操作符|-> |=>的property,如果antecedent一直未被触发,也一定不会出现CEX,此时为空成功vacuous success。vacuous在Simulation中经常出现,因为施加的有限激励,没有触发antecedent成功。但是在Formal中,需要引起注意。
Cover Points: Covered: 覆盖 Uncovered: 未覆盖
the SVA differences
在Simaltion和Formal中,SVA的使用略有不同:
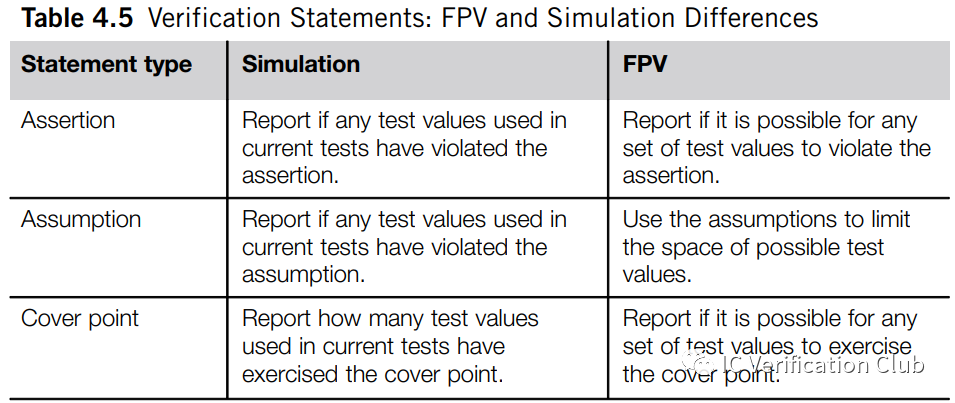
Simulation中的assume和assertion作用相同,不起到约束的作用;而Formal中,assume实现约束的作用;对于Simulation的vacuous success,并不会报错引起用户注意,一般建议对property同时做assert和cover处理。
Sequential depth
Sequential depth:也就是上文提及到的Cycle depth;较大的Sequential depth,容易产生inconclusive的结果。
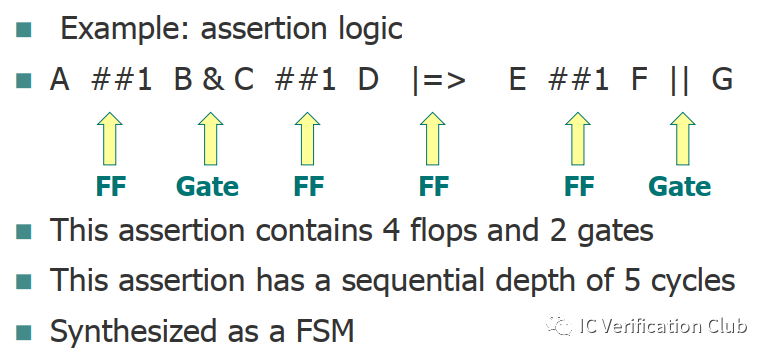
Assertion Logic Contributes to State Space
COI
COI(CONES OF INFLUENCE):COI是Formal工具对property的逻辑威廉希尔官方网站 映射,也被称作Logic Cones逻辑锥。COI包含property的所有input和state element,这些决定了不同的输出结果。
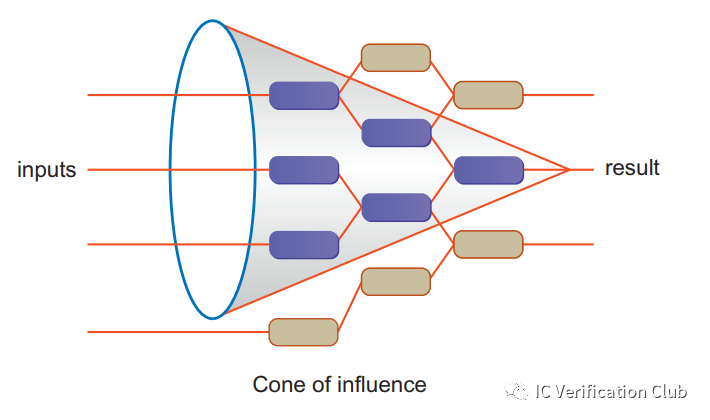
Formal工具对一个property解析生成的COI Schematic:
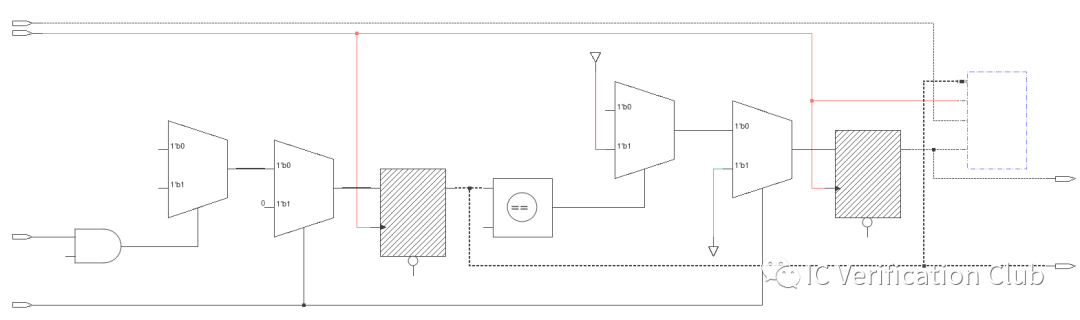
从用户角度,我们不必关心一个property的COI具体是什么样子;用户创建的所有property的COI集合对DUT RTL的覆盖情况,类似于Simulation中的Code coverage,称为Property Density。
The suggestion of SVA for Formal
formal model从SVA中提取,所以SVA的书写方式,也会影响Formal的效率,推荐的SVA Coding Guidelines可以参考《VC_Formal_UG》Appendix B。下面介绍一些常见的assertion”技巧“:
uniform format
assertion的书写,需要遵循同一的格式,每条assertion有相应的文档记录;每条property都有可读性的lable标注;可以采用一些宏定义,简化assertion的书写,参考:prim_assert.sv[4] 当assertion的clock,reset都是同一个时,可以声明default clocking 和 default disable iff,简化书写。
Immediate VS Concurrent
虽然立即断言在一些情况下等效于并发断言,如下:
// Concurrent Assertion assert_overfloat_func: assert property (`clk_rst $rose(overfloat) |-> $past(cnt==4'hF)); // Immediate Assertion always @(posedge clk ) if($rose(overfloat)&&(rstn==1)) assert_overfloat_func_2:assert($past(cnt==4'hF));
但是建议使用并发断言,Formal工具对蕴含操作符的支持更好。
Try use implication
不建议直接对sequence进行断言,sequence会在每个cycle都被检查;推荐使用蕴含操作符的方式。
// BAD property send_header_payload; @(posedge clk) disable iff(reset) (enable ##1 header ##1 payload[*16]); endproperty // GOOD property send_header_payload; @(posedge clk) disable iff(reset) $rose(enable) |=> header ##1 payload[*16]; endproperty
SVA Modeling Layer Code
可以通过增加Auxiliary Code,简化property的书写难度;如下:
module assert_top (input rstn, input clk, input A,
input, B, input C, input wr, input rd );
// Requirement: inputs A, B, C are mutually exclusive
wire [2:0] my_bus = {A,B,C};
a_abc_mutex: assert property (@(posedge clk) $onehot0(my_bus) );
// Requirement: No more than 5 outstanding wr’s (without a rd)
// and no rd before wr
reg [2:0] my_cnt;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rstn)
if (!rstn) my_cnt <= 3’b000;
else
if ( wr && !rd) my_cnt <= my_cnt + 1;
else if (!wr && rd) my_cnt <= my_cnt – 1;
else my_cnt <= my_cnt;
a_wr_outstand_le5: assert property (@(posedge clk) my_cnt <= 3’d5 );
a_no_rd_wo_wr: assert property (@(posedge clk) !((my_cnt == 3’d0) && rd));
endmodule
use function
assertion中可以调用funciton。
// Compute next grant for round-robin scheme
function logic [3:0] fv_rr_next(logic [3:0] req,logic [3:0] gnt);
fv_rr_next = 0;
for (int i=1; (i<4); i++) begin
if (req[(fv_which_bit(gnt)+i)%4]) begin
fv_rr_next[(fv_which_bit(gnt)+i)%4] = 1;
break;
end
end
endfunction
Page81_rr_next: assert property (((opcode == NOP) &&
(|gnt == 1) && (|req == 1) && (|(req&gnt)==4'b0)) |=> (gnt == fv_rr_next(req,gnt)))
else $error("Violation of round robin grant policy.");
as SIMPLE as possible
将一个大的assertion才分为多个小的assertion
$rose(START) |=> (ENABLE && ~START && ~STOP)[*7] ##1 (ENABLE && ~START && STOP) |=> (~ENABLE && ~START && ~STOP); $rose(START) |-> ~ENABLE ##1 ENABLE; $rose(ENABLE) |-> (~START && ~STOP)[*7]; $rose(STOP) |-> ENABLE ##1 ~ENABLE; $fell(START) |=> ##5 $rose(STOP);
as SHORT as possible
尽量缩短Cycle Depth,使用[0:$]或者太大的时间delay不利于formal分析。
a5: assert property @(posedge clk) a |-> ( ##[0:$] b); a6: assert property (@(posedge clk) disable iff (~rst_n) A ##1 B |=> C ##[1:100] D );
use Systemverilog
采用可综合的systemvrilog语法,如interface,struct等,使用更便捷;像s_eventually, 在sv09才支持。
Formal Property Verification
以一个counter做简单的演示:
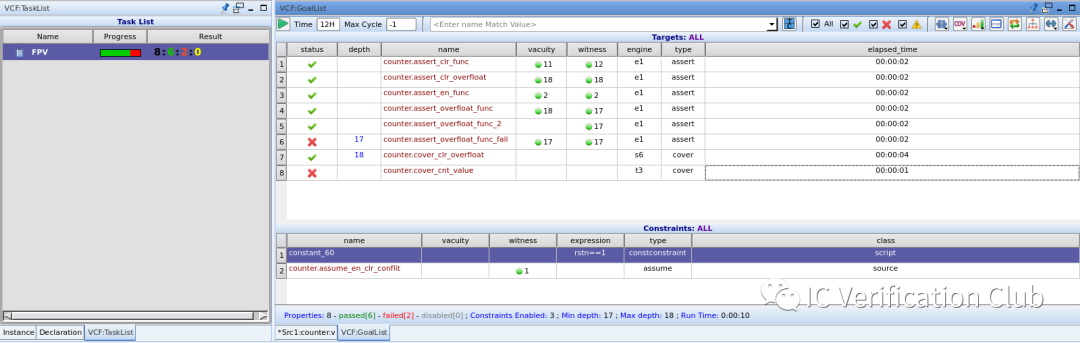
module counter( input clk, input rstn, input en, input clr, output cnt, output overfloat ); reg [3:0] cnt; reg overfloat; always@(posedge clk,negedge rstn) begin if(!rstn) cnt <= 4'b0; else if (clr) cnt <= 0; else if (en & (cnt!=4'hF)) cnt <= cnt + 1; end always@(posedge clk,negedge rstn) begin if(!rstn) overfloat <= 1'b0; else if (clr) overfloat <= 1'b0; else if (cnt==15) overfloat <= 1'b1; end `ifdef FPV `define clk_rst @(posedge clk) disable iff (!rstn) //ASSUME assume_en_clr_conflit: assume property (`clk_rst !(en && clr)); //COVER cover_clr_overfloat: cover property (`clk_rst $fell(overfloat)); cover_cnt_value: cover property (`clk_rst (cnt==20)); //ASSERT assert_clr_func: assert property(`clk_rst clr |=> ((overfloat==0)&&(cnt==0))); property p_en_func; int tmp; `clk_rst (en,tmp=cnt) |=> if(cnt!=4'hF) (tmp + 1 == cnt); endproperty assert_en_func: assert property(p_en_func); assert_clr_overfloat: assert property (`clk_rst $fell(overfloat) |-> $past(clr)); //PASS assert_overfloat_func: assert property (`clk_rst $rose(overfloat) |-> $past(cnt==4'hF)); //WRONG assertion assert_overfloat_func_fail: assert property (`clk_rst (cnt==4'hF) |=> overfloat); //Immediate Assert always @(posedge clk ) if($rose(overfloat)&&(rstn==1)) assert_overfloat_func_2:assert($past(cnt==4'hF)); `endif endmodule
Result: vacuity栏为property的先行算子成立的cycle depth。 witness栏为property的后续算子成立的cycle depth。对于assert_overfloat_func这个property,witness早于vacuity1个cycle,是因为$past()是对过去的判断。
Initial State 定义clk,rstn;从复位状态开始,Formal工具自动对input信号灌入激励。
# Clock Definitions create_clock clk -period 100 # Reset Definitions create_reset rstn -sense low # Initialisation Commands sim_run -stable sim_save_reset
ASSUME
增加了en和clr不可能同时为高的约束。
COVER
增加一些关心的cover point,工具可以快速地跑出对应波形:例如$fell(overfloat)的cover:
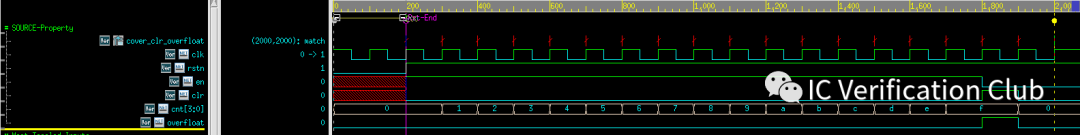
200ns:完成复位 2000ns:cover point match(注意采样的上升沿前的数据)
对于(cnt==20))则是uncover,cnt最大值为15。
ASSERT
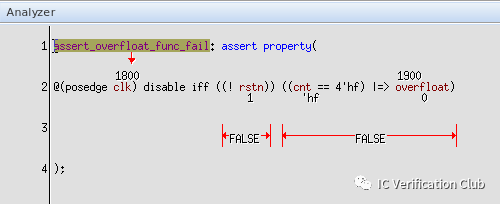
assert_overfloat_func_fail: assert property (`clk_rst (cnt==4'hF) |=> overfloat); 这个propery断言失败,被工具找到了一个CEX: 当cnt==4'hF时,同时拉高clr,overfloat就不会为高了。
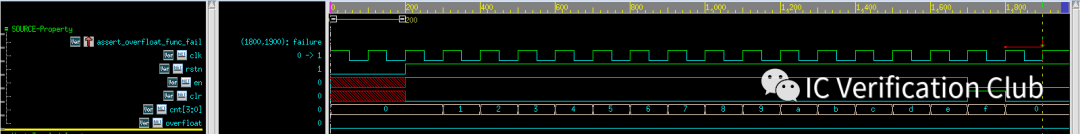 在这里插入图片描述
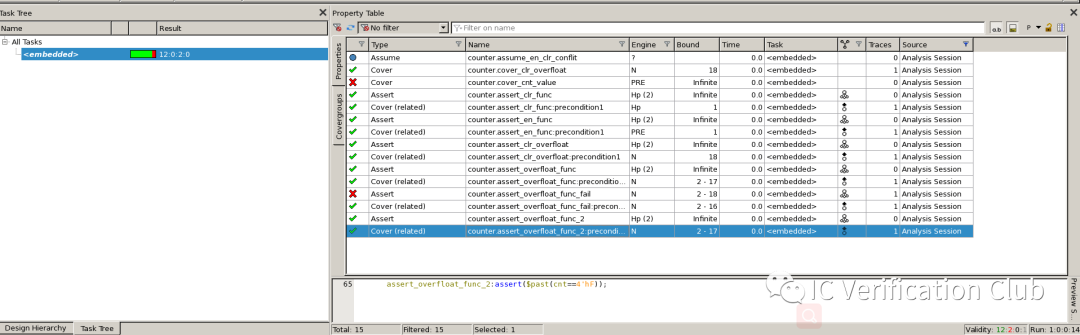
在这里插入图片描述
assertion annotation:
**ENGINE** Type栏的e1,s6,t3为算法引擎的代号;工具会根据property的特性选择合适的算法,调用相应的引擎处理; VC Formal中的engines:
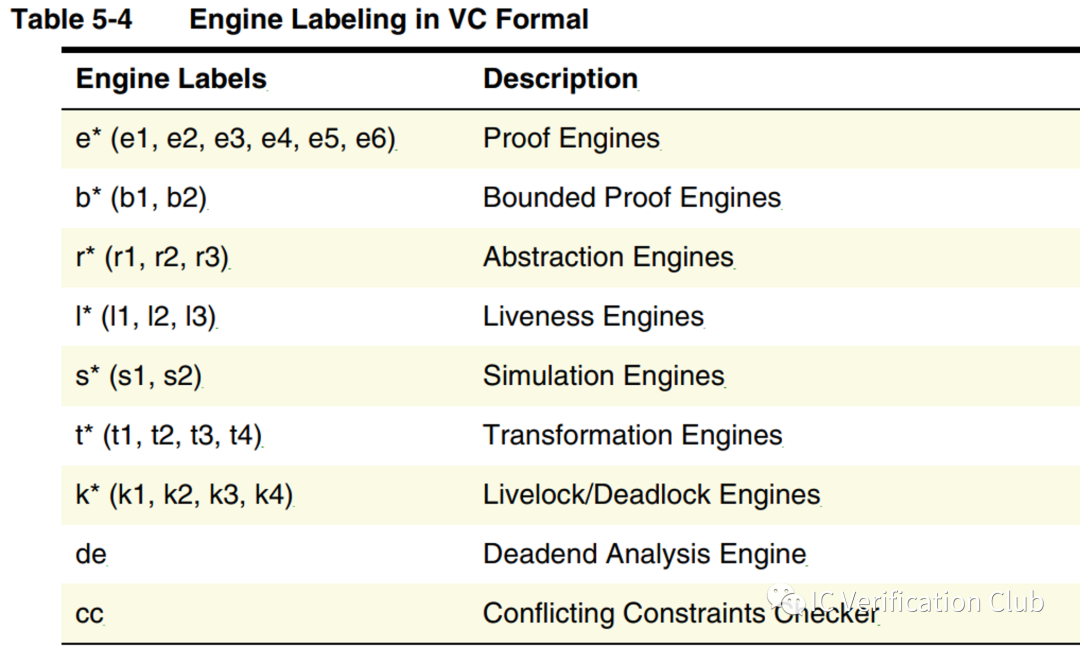
常见算法为:
• Binary Decision Diagrams or BDD
• "SATisfiability" Proofs or SAT
• Bounded Model Checking or BMC
• Craig Interpolation, usually shortened to "Craig"
• Property Directed Reachability or PDR
一般使用工具默认分配的engine,当然用户也可以自己指定;VC Formal提供了多种引擎编排的recipes,适用FPV不同的使用场景。
JasperGold Result
CEX wave:
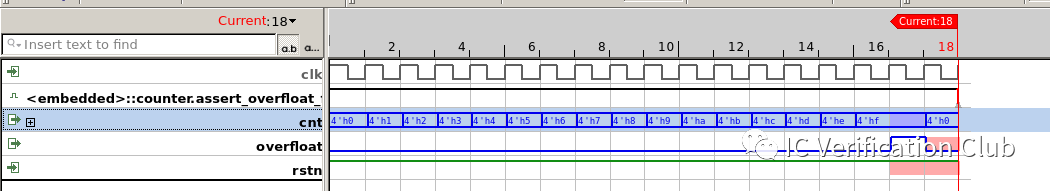
JasperGold中的engines:
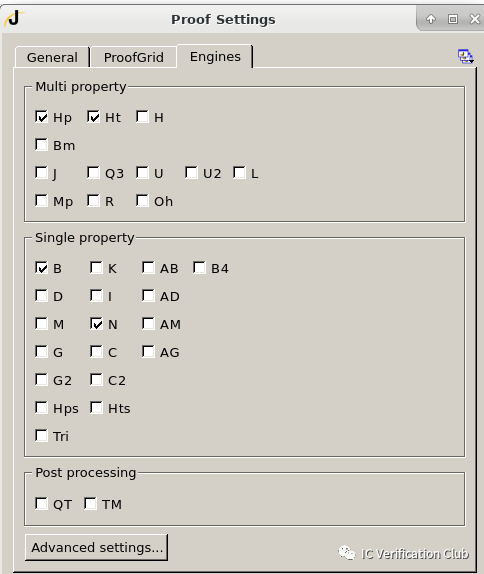
FPV的使用场景
design exercise FPV
FPV不需要搭建平台和手动施加激励,适合快速的在一些新设计的RTL上跑一些基础功能;例如上一节$fell(overfloat))这个cover point,如果通过Simulatin,需要搭建testbench并详尽地施加每一拍的激励;而使用Formal,设计人员不需要关注整个过程,只关注最终结果,工具会自动施加相应的激励并达到你想要的结果。
所以当你有以下需求时,可以考虑使用design exercise FPV:
1. 对于新设计的模块,想要跑一些基础功能进行确认
2. 在验证人员的验证平台还没有准备好时,需要自己提前做一些简略地验证
3. 接手遗留的RTL代码,可以跑一下FPV,结合波形加深对特定功能的理解
设计人员自己跑FPV,对RTL内部细节很了解;思路一般是:首先增加感兴趣的cover point;再添加一些assumption,可以过度约束;先跑出一些简单功能的波形;增加一些assertion,做检查;接着添加一些复杂功能的assertion和cover point,并逐渐放宽assumption;跑FPV并不是可以一次性把所有property都写完备,需要"wiggle"几轮,多次调试property;
有些公司对IP开发有额外的断言标准要求,例如property应该占RTL总代码行数的三分之一;这些property既可以用于formal,也可以用于simulation。《Assertion-Based Design》,《Creating Assertion-Based IP》书籍中介绍了相关经验。
Bug hunting FPV
当你有以下需求时,可以考虑使用Bug hunting FPV:
1. 你所验证的模块有很多corner cases,需要额外的FPV验证保证完备性
2. Simulation回归random case时,陆续发现新的error,需要额外的FPV验证提高置信度
3. 对于一个成熟的模块,加了一个新的feature,需要额外的FPV验证
Bug hunting FPV是Simulation的补充验证手段,采用更高层级的assertion,加入过约束,将注意力集中于某一个功能点;
full proof FPV
对一个设计只采用FPV进行验证,保证设计功能100%符合spec;这个从理论上是完全可行的,也是Formal Verification的初衷:只要property是完备的,正确的,相对于RTL,就可以建立一个golden model,遍历RTL的所有状态空间,保证100%正确。当你满足以下条件时,可以采用full proof FPV:
1. 待测设计有一个详细的规格书或者一个包含所有功能点的表格
2. 待测设计是一个标准接口,可以采用商业的AIP进行验证
对于full proof FPV,每种Formal工具都有推荐的sign-off流程,来保证验证的完备。
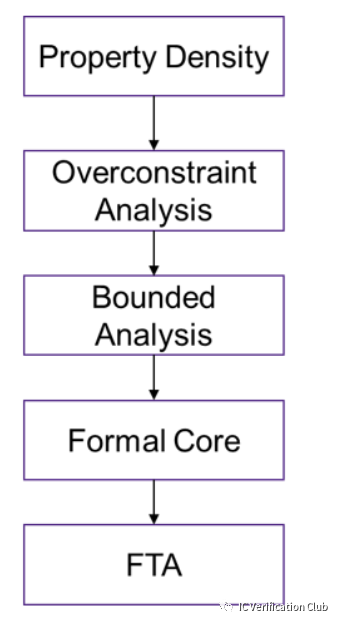
VC Formal的推荐流程如下:
JasperGold的推荐流程如下:
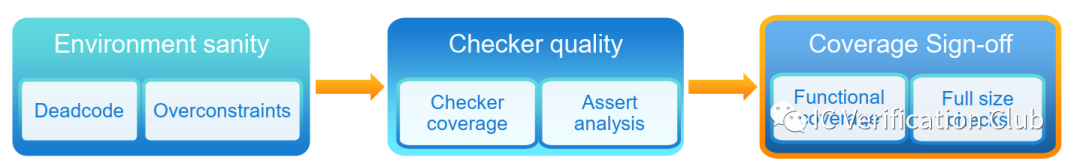
通过收集覆盖率,保证property的完备,完成sign-off工作。具体后文介绍。
APPs
formal tool除了FPV,还提供了其他适用不同场景的APPs,如对于pinmux可以采用connectivity连通性检查,对于寄存器的访问采用register检查,对于一块mem,是否存在其他非法访问路劲,可以才用security检查;这一类app都是FPV的衍生,通过提供一文件或约束,工具自动产生property,调用最佳engine处理。相较于FPV,学习成本低。对于汽车产品,有额外的Functional Safety要求,工具会自动对rtl注错分析其影响结果。
VC Fomrla Apps:
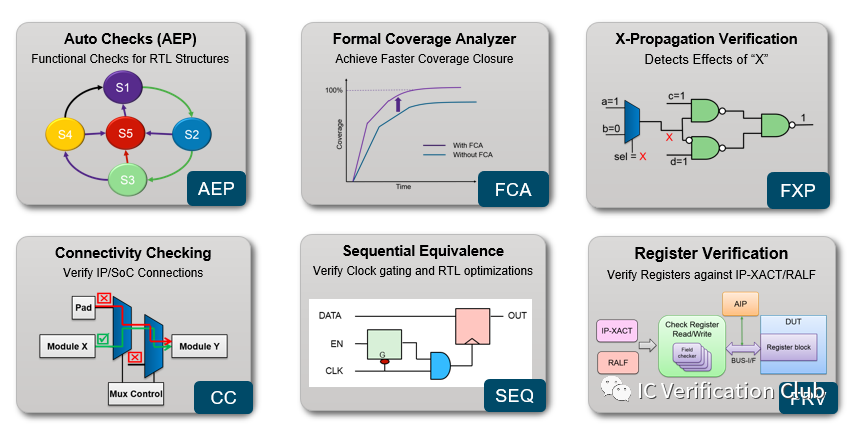
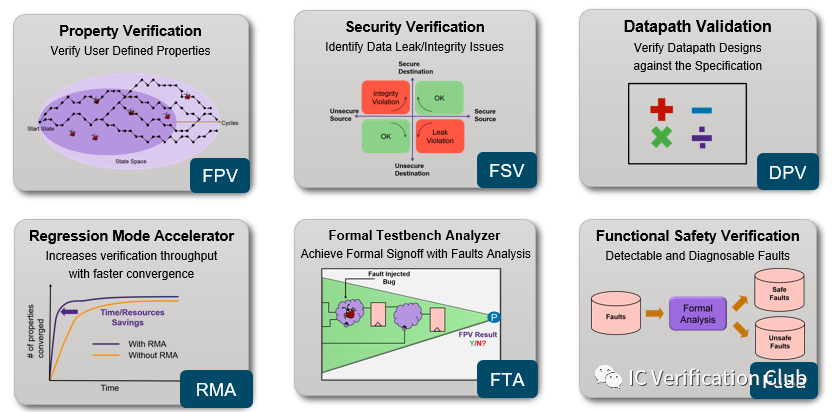
对于以上Apps, 可能除了DPV, JasperGold都有对应的Apps.
审核编辑:刘清
- 相关推荐
- 处理器
- 逻辑威廉希尔官方网站
- SVA
- DUT
- FPV
-
什么是FPV?怎样去搭建FPV验证环境呢?2022-06-27 0
-
搭建FPV验证环境之创建assert与执行FPV简析2022-06-27 0
-
一、什么是FPV?2022-06-28 0
-
FPV设计的状态空间主要由什么因素决定的2022-09-14 0
-
A Roadmap for Formal Property2009-07-18 646
-
Advanced Formal Verification2009-07-21 538
-
Functional Verification Coverage Measurement and Analysis2009-07-25 1070
-
AVM Based Unified Verification2010-07-04 920
-
FPV58口系列智能涡街流量计技术资料2010-08-26 736
-
新思科技升级Verification Continuum平台继续引领技术2019-06-11 4814
-
分享一些形式验证(Formal Verification)的经典视频2023-02-11 843
-
Formal Verification的基础知识2023-05-25 2676
-
数字验证中Formal Verification在国内的应用以及前景如何?2023-06-26 1381
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

