

SimpleFOC之多路PWM驱动,相电流监测2
电子说
1.3w人已加入
描述
低侧电流测试
低侧电流检测可能是最常见的电流检测技术。主要原因是它既不需要高性能PWM抑制电流检测放大器(如在线检测放大器),也不需要支持高压的放大器(如高侧放大器)。
采样电阻始终置于低侧MOSFET和地之间,确保放大器的端子上始终具有非常低的电压。这种方法的主要缺点是,由于只有相应的低侧mosfet开启时,通过采样电阻的电流才是相电流,而我们只能在这些时刻测量到相电流。PWM频率通常为20至50 kHz,这意味着低侧MOSFET每秒开关20000至50000次,因此PWM设置和ADC采集之间的同步非常重要。
目前这个在开发中。
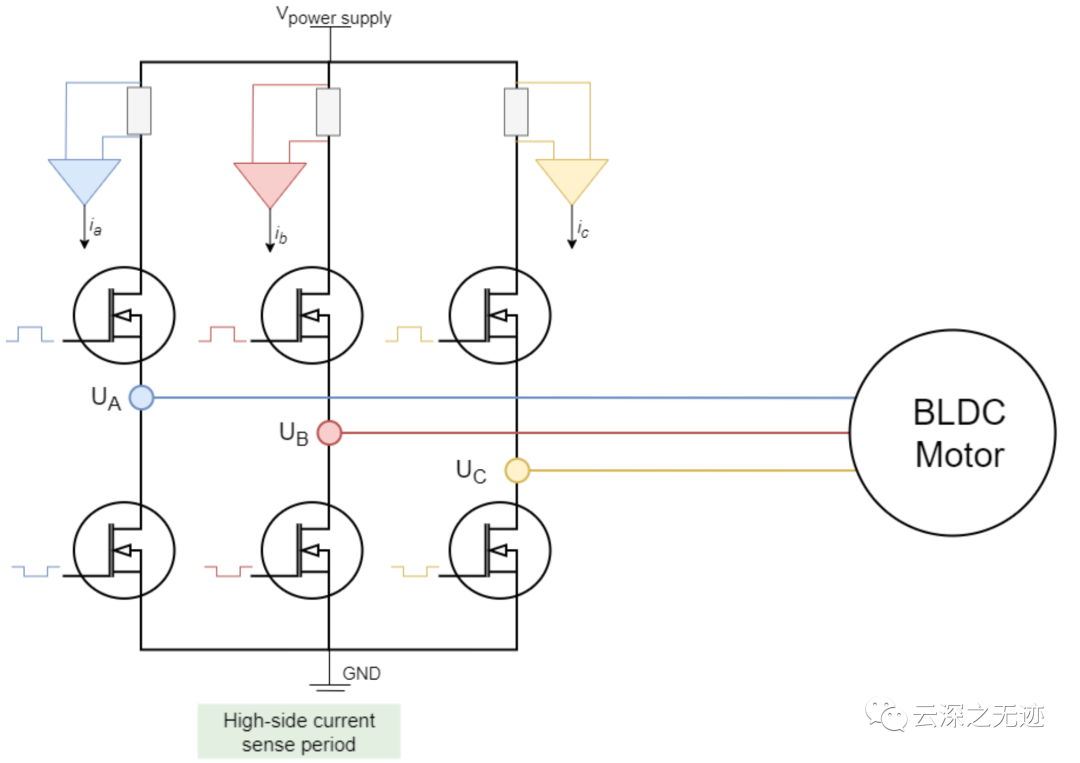
这个是高测测量一般也不用
https://www.ti.com.cn/product/cn/INA240
https://www.obk20.com/analog/202007151246626.html
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/401573207
https://www.sohu.com/a/439655421_468638
https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1753450617334241521&wfr=spider&for=pc
https://m.obk20.com/article/1107269.html
https://www.obk20.com/d/1412716.html
// IN1 pwm1 9 27
// IN2 pwm2 6 26
// IN3 pwm3 5 25
// INH1 enable1 8 12
// INH2 enable2 7 13
// INH3 enable3 4 14
// in-line current sense - phase 1/A 35
// in-line current sense - phase 1/C 34
#include
class LowPassFilte
{
public:
LowPassFilte(float Tf); // 低通滤波器时间常量
~LowPassFilte() = default;
float operator()(float x);
float Tf; //!< 低通滤波器时间常量
protected:
unsigned long timestamp_prev; //!< 上次执行时间戳
float y_prev; //!< 经过上次执行后过滤到的值
};
LowPassFilte::LowPassFilte(float time_constant)
: Tf(time_constant), y_prev(0.0f)
{
timestamp_prev = micros();
}
float LowPassFilte::operator()(float x)
{
unsigned long timestamp = micros();
float dt = (timestamp - timestamp_prev) * 1e-6f;
if (dt < 0.0f || dt > 0.5f)
dt = 1e-3f;
float alpha = Tf / (Tf + dt);
float y = alpha * y_prev + (1.0f - alpha) * x;
y_prev = y;
timestamp_prev = timestamp;
return y;
}
LowPassFilte LF_a(0.01); // 原始数据滤波器
LowPassFilte LF_b(0.01); // A相电流滤波器
LowPassFilte LF_c(0.01); // C相电流滤波器
// AS5600编码器支持spi,iic和模拟量三种数据传输方式,这里用iic(同时也是最常用的方式)
// magnetic sensor instance - I2C
MagneticSensorI2C sensor = MagneticSensorI2C(AS5600_I2C);
TwoWire I2Cone = TwoWire(0);
// BLDC motor & driver instance
BLDCMotor motor = BLDCMotor(11);
BLDCDriver3PWM driver = BLDCDriver3PWM(27, 26, 25, 12, 13, 14);
InlineCurrentSense Cs_motor(0.001, 50.0, 35, 36, 34);
// voltage set point variable
float target_voltage = 5.0;
// instantiate the commander
Commander command = Commander(Serial);
void doTarget(char *cmd)
{
command.scalar(&target_voltage, cmd);
}
void setup()
{
// initialise magnetic sensor hardware
I2Cone.begin(18, 5, 400000);
sensor.init(&I2Cone);
// link the motor to the sensor
motor.linkSensor(&sensor);
// power supply voltage
driver.voltage_power_supply = 12;
driver.init();
motor.linkDriver(&driver);
// aligning voltage
motor.voltage_sensor_align = 5;
// choose FOC modulation (optional)
motor.foc_modulation = FOCModulationType::SpaceVectorPWM;
// set motion control loop to be used
motor.controller = MotionControlType::torque;
// use monitoring with serial
Serial.begin(115200);
// comment out if not needed
motor.useMonitoring(Serial);
// initialize motor
motor.init();
// align sensor and start FOC
motor.initFOC();
// add target command T
command.add('T', doTarget, "target voltage");
Serial.println(F("Motor ready."));
Serial.println(F("Set the target voltage using serial terminal:"));
_delay(1000);
Cs_motor.init();
}
void loop()
{
// main FOC algorithm function
// the faster you run this function the better
// Arduino UNO loop ~1kHz
// Bluepill loop ~10kHz
motor.loopFOC();
// Motion control function
// velocity, position or voltage (defined in motor.controller)
// this function can be run at much lower frequency than loopFOC() function
// You can also use motor.move() and set the motor.target in the code
motor.move(target_voltage);
// Cs_motor.getPhaseCurrents();
Serial.print(LF_b((Cs_motor.getPhaseCurrents()).a));
Serial.print(",");
Serial.println(LF_c((Cs_motor.getPhaseCurrents()).c));
// Serial.print(LF_a(analogRead(35)));
// Serial.print(",");
// Serial.print(LF_b((3.3 * ((float)analogRead(35) - 1930) / 4096.0) * 20.0));
// Serial.print(",");
// Serial.println(LF_c((-3.3 * ((float)analogRead(34) - 1930) / 4096.0) * 20.0));
// user communication
command.run();
}
声明:本文内容及配图由入驻作者撰写或者入驻合作网站授权转载。文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表电子发烧友网立场。文章及其配图仅供工程师学习之用,如有内容侵权或者其他违规问题,请联系本站处理。
举报投诉
-
小波变换在伺服驱动器相电流信号处理中的应用研究_魏思维2017-03-15 810
-
SimpleFOC之多路PWM驱动,相电流监测12023-04-24 3299
-
线电流和相电流的关系2023-12-01 10524
-
无刷电机相电流比母线电流大?2016-01-19 0
-
三相电流跟踪型PWM逆变威廉希尔官方网站2009-09-09 2637
-
基于组合载波控制的三相电流型PWM逆变器研究_黄钰2016-12-30 880
-
一个PWM控制周期如何取得两相电流数据2017-09-13 12833
-
一个PWM波形内采集两相电流ADC数据2017-09-18 18209
-
什么是相电流和线电流2020-03-11 195087
-
SimpleFOC -foc电流-力矩控制代码2021-12-16 688
-
SimpleFOC -位置控制代码2022-01-14 685
-
步进电机相电流怎么测2023-12-13 4105
-
怎么区分相电流与线电流的区别2024-07-17 4434
-
相电流和线电流的相位关系2024-07-17 2682
-
负载电流是线电流还是相电流2024-10-08 1086
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

