

光电子学领域新成员——铋/锑卤氧化物和硫卤化物
电子说
描述
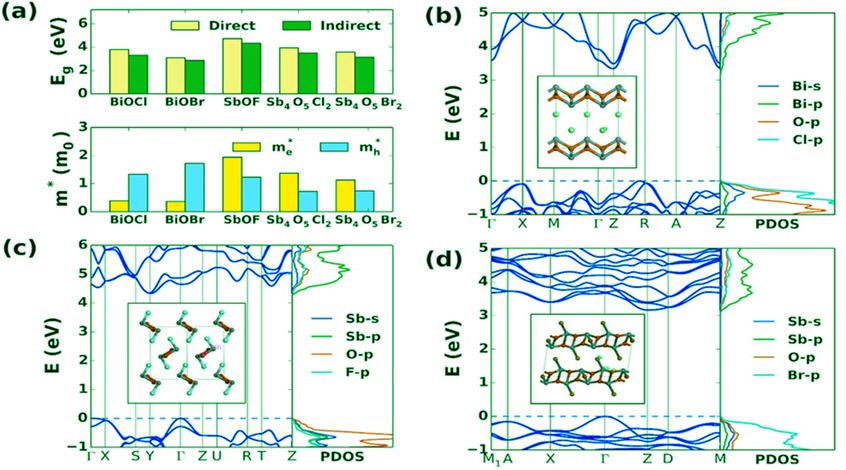
近十年来,ns2阳离子(如Pb2+和Sn2+)基卤化物(如混合钙钛矿太阳能吸收剂等)已成为最令人兴奋的光电子材料新类别之一。这些材料不仅在某些情况下表现出前所未见的性能,且可能以其优异的性能(如对缺陷的极端耐受性)打开一片新天地。然而,此类材料才刚出现不久,其很多化合物尚未得到充分的探索。来自吉林大学、密苏里大学和阿肯色州立大学的科研人员,采用连贯第一性原理法研究了一系列铋/锑卤氧化物和硫卤化物的性质及其规律。他们惊奇地发现,一些铋基硫卤化物(带隙范围为1.5~2eV)有望用于太阳能电池和室温辐射探测器;而它们的卤氧化物(带隙高于3 eV),则由空穴传导,若被掺杂,可用作透明导电材料。在此基础上,合作者们进而探讨了这些化合物的电子结构及其与晶体几何结构的关系,以及对带边扩散和载流子有效质量的影响。作者们据此认为,有必要对该类潜在的光电子应用材料作进一步实验研究,为其在太阳能电池等方面的应用奠定基础。该文近期发表于npj Computational Materials 4: 14 (2018); doi:10.1038/s41524-018-0071-1。

Bismuth and antimony-based oxyhalides and chalcohalides as potential optoelectronic materials
Zhao Ran, Xinjiang Wang, Yuwei Li, Dongwen Yang, Xin-Gang Zhao, Koushik Biswas, David J. Singh& Lijun Zhang
In the last decade the ns2 cations (e.g., Pb2+ andSn2+)-based halides have emerged as one of the most exciting new classes of optoelectronic materials, as exemplified by for instance hybrid perovskite solar absorbers. These materials not only exhibit unprecedented performance in some cases, but they also appear to break new ground with their unexpected properties, such as extreme tolerance to defects. However, because of the relatively recent emergence of this class of materials, there remain many yet to be fully explored compounds. Here, we assess a series of bismuth / antimony oxyhalides and chalcohalides using consistent first principles methods to ascertain their properties and obtain trends. Based on these calculations, we identify a subset consisting of three types of compounds that may be promising as solar absorbers, transparent conductors, and radiation detectors. Their electronic structure, connection to the crystal geometry, and impact on band-edge dispersion and carrier effective mass are discussed.
-
金属氧化物太阳能电池研究取得突破2016-03-07 0
-
什么是金属卤化物灯2010-02-08 4389
-
金属卤化物灯原理详解2011-02-25 5380
-
金属卤化物灯使用说明2018-01-18 8990
-
金属卤化物灯安全吗_金属卤化物灯有哪些优缺点2018-01-18 9062
-
金属卤化物灯有哪些优缺点_金属卤化物灯工作原理2018-01-19 17742
-
金属卤化物灯常见故障有哪些2018-01-19 21789
-
金属卤化物灯怎么接线_金属卤化物灯接线图2018-01-19 39293
-
金属卤化物灯启动不了_金属卤化物灯怎么修2018-01-19 11400
-
金属卤化物灯原理2019-03-18 6737
-
基于二维材料的压电光电子学器件综述2023-07-31 1896
-
零维有机-无机杂化金属卤化物的溶液合成、光物理性质及光电应用2023-11-14 1639
-
铅框架 - HengHui Ag Plate RoHS/卤化物2024-01-05 161
-
随附 - 8290 RoHS/卤化物测试报告2024-02-25 158
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

